Redis - 아키텍쳐
이 포스트는 Redis 운영 시 알아야 할 아키텍쳐에 관해 알아본다.
- 1. Redis 아키텍쳐
- 2. 시스템, Disk 사양
- 3. 메모리 운영기법
- 4. LazyFree
- 5. 데이터 Persistence(저장)
- 6. Copy on Write
- 7. Benchmark For Redis
- 8. 관리 명령어 (redis-cli)
- 9. Data Export, Import
- 10. Redis Serialization Protocol & Mass Insertion
- 11. redis-cli option
1. Redis 아키텍쳐
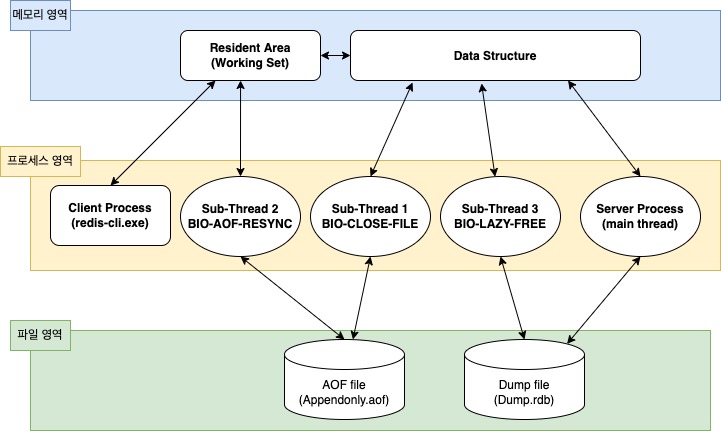
1.1. 메모리 영역
- Resident Area
- 사용자가 Redis 서버에 접속해서 처리하는 모든 데이터가 가장 먼저 저장되는 영역
- 실제 작업이 수행되는 공간
- Data Structure
- 서버 운영 시 발생하는 정보와 서버 상태를 모니터링하기 위해 수집한 상태 정보가 저장되고 관리되는 메모리 공간
메모리 영역 확인
127.0.0.1:6379> info memory
# Memory
used_memory:1459888 # 현재 할당된 레디스 서버 크기 (byte)
used_memory_human:1.39M # 사용자가 사용 중인 레디스 메모리 크기
used_memory_rss:802816
used_memory_rss_human:784.00K
used_memory_peak:1476848
used_memory_peak_human:1.41M
used_memory_peak_perc:98.85%
used_memory_overhead:1194136
used_memory_startup:1192144
used_memory_dataset:265752
used_memory_dataset_perc:99.26%
allocator_allocated:1442768
allocator_active:771072
allocator_resident:771072
total_system_memory:17179869184 # 시스템 메모리 총 크기
total_system_memory_human:16.00G # 사용자가 사용 가능한 시스템 메모리 크기
used_memory_lua:31744
used_memory_vm_eval:31744
used_memory_lua_human:31.00K
used_memory_scripts_eval:0
number_of_cached_scripts:0
number_of_functions:0
number_of_libraries:0
used_memory_vm_functions:32768
used_memory_vm_total:64512
used_memory_vm_total_human:63.00K
used_memory_functions:216
used_memory_scripts:216
used_memory_scripts_human:216B
maxmemory:0 # maxmemory 파라미터에서 설정된 메모리 크기
maxmemory_human:0B # 사용자가 실제 사용 가능한 레디스 메모리 크기
maxmemory_policy:noeviction
allocator_frag_ratio:0.53
allocator_frag_bytes:18446744073708879920
allocator_rss_ratio:1.00
allocator_rss_bytes:0
rss_overhead_ratio:1.04
rss_overhead_bytes:31744
mem_fragmentation_ratio:0.56
mem_fragmentation_bytes:-639952
mem_not_counted_for_evict:0
mem_replication_backlog:0
mem_total_replication_buffers:0
mem_clients_slaves:0
mem_clients_normal:1776
mem_cluster_links:0
mem_aof_buffer:0
mem_allocator:libc
active_defrag_running:0
lazyfree_pending_objects:0
lazyfreed_objects:0
실시간으로 사용 중인 메모리 크기 확인
$ redis-cli -r 10 -i 1 info | grep used_memory_human
used_memory_human:1.43M
used_memory_human:1.42M
used_memory_human:1.42M
used_memory_human:1.42M
used_memory_human:1.43M
used_memory_human:1.43M
used_memory_human:1.42M
used_memory_human:1.42M
used_memory_human:1.42M
-r <count>command 를 실행할 횟수
-i <delay>다른 command 호출 사이의 delay 를 seconds 단위로 설정
실시간으로 사용 가능한인 시스템 메모리 크기 확인
$ redis-cli -r 3 -i 1 info | grep total_system_memory_human
total_system_memory_human:16.00G
total_system_memory_human:16.00G
total_system_memory_human:16.00G
실시간으로 실제 사용 가능한 레디스 메모리 크기 확인
$ redis-cli -r 3 -i 1 info | grep maxmemory_human
maxmemory_human:0B
maxmemory_human:0B
maxmemory_human:0B
메모리 영역에 대한 Hit 와 Misses 확인
> info stats
# Stats
total_connections_received:7
total_commands_processed:49
...
keyspace_hits:7 # 메모리로부터 동일한 데이터가 발견된 경우 hits 증가
keyspace_misses:0 # 동일한 데이터를 발견하지 못한 경우 misses 증가
1.2. 파일 영역
- AOF 파일
- Redis 는 모든 데이터를 메모리 상에 저장/관리하는 인메모리 기반이지만 중요 데이터의 경우 지속적인 저장이 필요
이 때 사용되는 디스크 영역이 AOF 파일 (스냅샷 데이터)
- Redis 는 모든 데이터를 메모리 상에 저장/관리하는 인메모리 기반이지만 중요 데이터의 경우 지속적인 저장이 필요
- DUMP 파일
- 소량의 데이터를 일시적으로 저장할 때 사용되는 파일
1.3. 프로세스 영역
- Server Process
- redis-server.exe 혹은 redis-sentinel.exe 에 의해 활성화되는 프로세스
- Redis 인스턴스 관리
- 사용자가 요구한 작업 수행
- 4개의 멀티 스레드로 구성됨
main thread: Redis 서버에서 수행되는 대부분의 명령어와 이벤트를 처리sub thread 1 (BIO-Close-File): AOF(Append Only File) 에 데이터를 rewrite 할 때 기존 파일은 close 하고 새로운 AOF 파일에 write 할 때 사용sub thread 2 (BIO-AOF-Resync): AOF 에 write 할 때 사용sub thread 3 (BIO-Lazy-Free):unlink,flushall,flushdb명령어 실행 시 빠른 성능을 보장하기 위해 백그라운드에서 사용됨
- Client Process
- redis-cli.exe 혹은 사용자 애플리케이션에 의해 실행되는 명령어를 실행하기 위해 제공되는 프로세스
2. 시스템, Disk 사양
2.1. 노드 수 (# of nodes per cluster)
redis 서버 구축 시 Master 서버 1대, Slave 서버 1대, Sentinel 서버 1대 이렇게 최소 3대의 서버가 필요하다.
Sentinel 서버
일반적으로 운영 환경은 Master / Slave 로 구성이 되는데 운영 중 예기치못한 이슈로 Master 가 다운되면 Slave 를 Master 로 올리고 클라이언트가 새로운 Master 에 접속할 수 있어야 한다.
Sentinel 은 Master 와 Slave 서버의 네트워크 통신이 가능한지 체크하고 있다가 Master 에서 통신이 되지 않으면 자동으로 Slave 를 Master 로 올린다.
Slave 가 여러 대인 경우 다른 Slave 서버가 새로운 Master 로부터 데이터를 받을 수 있도록 재구성하고,
기존 Master 가 구동되는 경우 Slave 로 전환하여 새로운 Master 로부터 데이터를 받을 수 있도록 구성함
Master / Slave 서버는 실제 데이터를 처리하는 서버이므로 최적화된 서버 사양이 좋고,
Sentinel 서버는 사용자 데이터를 처리하는 용도는 아니므로 최소 사양으로 구성하는 것이 좋다.
2.2. CPU core 수 (# of cores per node)
각 서버당 CPU core 수를 고려할 때는 수많은 세션에서 초당 10만 ~ 20만건 이상의 데이터를 빠르게 read/write 하는 환경을 고려해야 한다.
정답은 없지만 최근 판매되는 Hardware server 들의 최소 사양이 4 core 인점을 감안하면 아래와 같이 정리가 가능하다.
- small biz. 환경: 4 core 이하
- medium biz. 환경: 4 ~ 8 core 이하
- big biz. 환경: 8 ~ 16 core 이상
2.3. RAM 크기
Redis 서버를 위한 최소 권장 사양은 14~15GB 이다.
하나의 서버가 16GB 메모리라면 대부분을 Redis 서버가 사용할 수 있어야 한다는 의미이므로, 하나의 서버에 웹서버 등과 같은 SW 를 함께 설치하는 것은 바람직하지 않다.
RAM 의 크기는 사용자 세션수, 처리하는 데이터양, 처리방법(batch, realtime), 초당 데이터 발생량 등을 고려해야 한다.
- small biz. 환경: 16GB 이하
- medium biz. 환경: 32 ~ 64GB 이하
- big biz. 환경: 64 ~ 128GB 이상
2.4. Storage 타입
저렴한 비용으로 데이터를 저장/관리하는 방법은 SATA 타입의 디스크 저장장치를 사용하는 것이지만,
SATA 타입 디스크보다 5~100배 이상의 빠른 read/write 가 가능한 SSD 타입의 저장 장치를 권장한다.
2.5. Storage 크기 (Persistent Storage)
Storage 크기를 고려할 때는 초당 발생량, 저장 보관 빈도(년/월/일), 저장할 총 데이터 양, 운영/관리를 위해 요구되는 디스크 공간 등을 고려해야 한다.
- 최소 Storage 크기: 사용자 데이터 총 크기 + (RAM 크기*3)
- 권장 Storage 크기: 사용자 데이터 총 크기 + (RAM 크기*6)
2.6. 네트워크
NoSQL 같은 빅데이터 처리 플랫폼은 Scale-out 을 기반으로 하는 분산, 복제 시스템이 기본 구성이므로 Scale-up 기반의 기존의 RDBMS 시스템 구성보다 네크워크 환경은 시스템 성능을 결정하는 중요한 요소 중 하나이다.
Redis 서버 운영을 위한 최소 네트워크 환경은 1G 이며, 적정 권장 환경은 10G 이상이다.
3. 메모리 운영기법
Redis 서버는 인메모리 기반의 데이터 저장/관리 기술로 개발된 대표적인 NoSQL 제품이다.
Redis 가 아닌 타 NoSQL 제품은 대부분 파일 시스템 기반의 데이터 저장/관리 기술로 개발되었기 때문에 모든 데이터들이 기본적으로 디스크 장치에 저장되고, 그 중 일부 데이터만 메모리 상에 임시로 저장된다.
디스크 저장 장치와 임시 메모리 영역인 버퍼 간의 유기적 역할 분담을 통해 데이터를 처리하기 때문에 디스크 저장장치로부터 지속적인 IO 가 발생하고, 이로 인해 빅데이터를 처리하는 경우 성능 지연 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
인메모리 기반은 모든 데이터를 메모리상에만 저장/관리하므로(=디스크 장치에는 어떤 데이터도 저장하지 않음) 파일 시스템에 비해 상대적으로 디스크 IO 가 발생하지 않아 빠른 성능을 기대할 수 있다.
물론 Redis 서버도 필요에 따라 중요 데이터를 DUMP, AOF 형태로 디스크 저장 장치에 저장할 수 있다.
Redis 서버의 시스템 메모리 크기는 제한적이고 상대적으로 사용자 데이터는 더 크기 때문에 모든 데이터를 100% 메모리에서 저장/관리할 수 없다.
이를 개선하기 위해 Redis 는 LRU (Least Recently Used) 알고리즘과 LFU (Least Frequently Used) 알고리즘을 제공한다.
3.1. LRU (Least Recently Used) 알고리즘
LRU 알고리즘은 가장 최근에 처리된 데이터들을 메모리 영역에 최대한 재배치시키는 알고리즘이다.
사용가능한 메모리 크기는 제한되어 있으므로 그 공간에 가장 최근에 입력/수정/삭제/조회된 데이터를 저장하고, 오래된 데이터는 메모리로부터 제거하는 방식이다.
오래된 데이터는 최근 데이터보다 재사용될 가능성이 적기 때문에 최근 데이터가 메모리에 위치하게 함으로써 성능 개선에 도움이 된다.
LRU 알고리즘으로 Redis 서버 인스턴스를 운영하기 위해서는 redis.conf 파일에 아래와 같은 파라미터를 설정해아 한다.
$ vi /usr/local/etc/redis.conf
...
maxmemory 3000000000 # redis 인스턴스를 위한 총 메모리 크기
maxmemory-sample 5 # LRU 알고리즘에 의한 메모리 운영 시 사용
3.2. LFU (Least Frequently Used) 알고리즘
LRU 알고리즘의 단점은 최근에 사용된 데이터들을 메모리 영역에 최대한 재배치하는 방식인데 그 데이터들이 모두 재사용되는 것은 아니라는 것이다.
LFU 알고리즘은 그 중 자주 참조되는 데이터만 배치하고 그 외의 데이터들은 메모리로부터 제거하여 자주 참조되는 데이터들이 메모리에 배치될 수 있도록 운영하는 방식이다.
LFU 알고리즘으로 Redis 서버 인스턴스를 운영하기 위해서는 redis.conf 파일에 아래와 같은 파라미터를 설정해아 한다.
$ vi /usr/local/etc/redis.conf
...
lfu-log-factor 10
lfu-decay-time 1
lfu-log-factor 의 가이드라인은 redis.io - eviction 에 정리되어 있다.
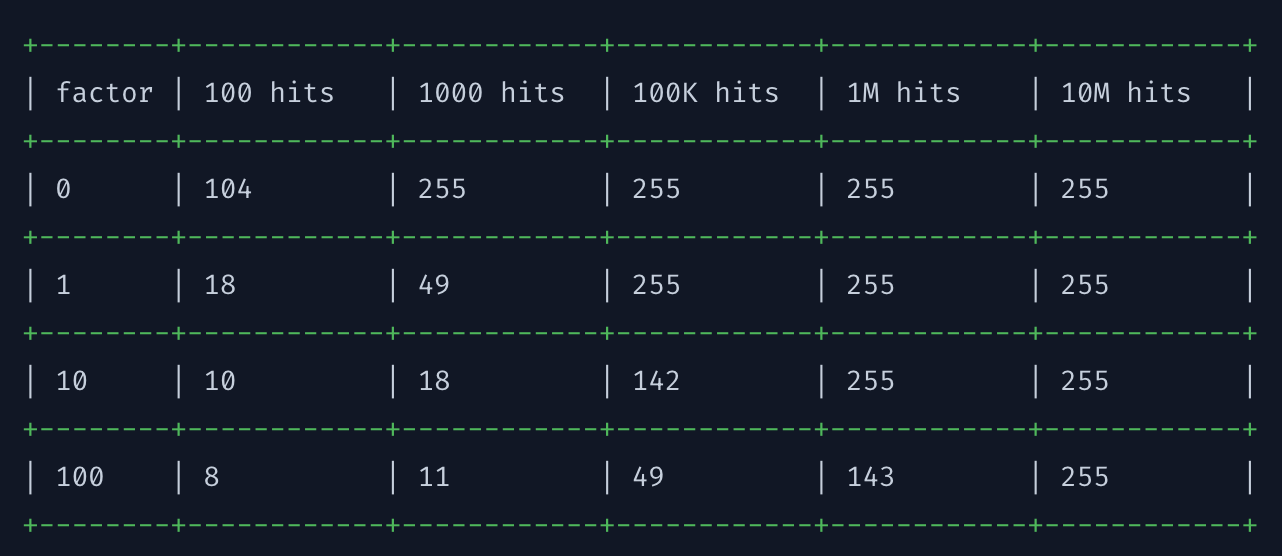
위 표에서 hits 값은 사용자가 메모리로부터 데이터를 재참조한 값으로 높을수록 좋다. (default 10)
LRU 알고리즘 적용 시 Redis 메모리 상태를 모니터링하는 방법은 아래와 같다.
$ redis-cli --lru-test 100
113500 Gets/sec | Hits: 113452 (99.96%) | Misses: 48 (0.04%)
119500 Gets/sec | Hits: 119499 (100.00%) | Misses: 1 (0.00%)
115750 Gets/sec | Hits: 115749 (100.00%) | Misses: 1 (0.00%)
116750 Gets/sec | Hits: 116750 (100.00%) | Misses: 0 (0.00%)
118000 Gets/sec | Hits: 118000 (100.00%) | Misses: 0 (0.00%)
116750 Gets/sec | Hits: 116750 (100.00%) | Misses: 0 (0.00%)
118500 Gets/sec | Hits: 118498 (100.00%) | Misses: 2 (0.00%)
115500 Gets/sec | Hits: 115500 (100.00%) | Misses: 0 (0.00%)
4. LazyFree
redis 인스턴스에 할당된 메모리 영역이 임계치에 도달하게 될 때 연속적인 범위의 key 값이 동시에 삭제되는 명령이 실행되면 메모리 부족과 프로세스 지연처리로 인해 성능 지연 문제가 발생한다.
이런 성능 지연 문제를 해소하는 방법은 Redis 인스턴스를 위한 메모리의 크기를 충분히 할당하는 것과 LazyFree 파라미터를 설정해주는 것이다.
LazyFree 파라미터는 별도의 백그라운드 스레드를 통해 입력과 삭제 작업이 지연되지 않고 연속적으로 수행될 수 있도록 해준다.
LazyFree스레드는 서버 프로세스의 4개 스레드 중 하나이다. 해당 내용은 위의 1.3. 프로세스 영역 을 참고하세요.
$ vi /usr/local/etc/redis.conf
...
lazyfree-lazy-eviction no # yes 권장
lazyfree-lazy-expire no # yes 권장
lazyfree-lazy-server-del no # yes 권장
slave-lazy-flush no # yes 권장
4.1. lazyfree-lazy-eviction
메모리가 full 이 되었을 때 연속적인 범위의 key 값을 삭제하면 기존 메모리에 저장되어 있던 데이터는 DEL 명령어에 의해 삭제되는데 이 작업은 서버 프로세스의 main thread 에 의해 실행되면서 블로킹 현상(=작업 지연 상태)이 발생한다.
이 파라미터를 yes 로 설정하면 DEL 명령어가 아닌 UNLINK 명령어가 실행되고 서버 프로세스의 sub-thread 3 에 의해 백그라운드에서 수행되므로 블로킹 현상을 피할 수 있다.
4.2. lazyfree-lazy-expire
EXPIRE 명령을 실행하면 메모리 상의 무효화된 key 값을 삭제하는데 내부적으로 DEL 명령어가 실행되면서 블로킹 현상이 발생한다.
이 파라미터를 yes 로 설정하면 UNLINK 명령어가 실행되면서 블로킹 현상을 피할 수 있다.
4.3. lazyfree-lazy-server-del
메모리 상에 이미 저장되어 있는 key 값에 대해 SET, RENAME 명령어를 실행하면 내부적으로 DEL 명령어가 실행되면서 블로킹 현상이 발생한다.
이 파라미터를 yes 로 설정하면 UNLINK 명령어가 실행되면서 블로킹 현상을 피할 수 있다.
4.4. slave-lazy-flush
slave 서버는 master 서버의 데이터 복제 시 변경된 부분에 대해서만 부분 복제를 하는 경우도 있지만 경우에 따라서는 기존 복제 데이터를 모두 삭제한 후 다시 복제하는 경우도 있다.
이 경우 기존 복제 데이터를 빠르게 삭제하고 동시에 다시 복제 작업을 빠르기 수행해야 한다.
이 파라미터를 yes 로 설정하면 복제 서버가 삭제 후 복제할 때 Flushall async 명령어로 삭제하기 때문에 빠른 동기화 작업이 가능하다.
5. 데이터 Persistence(저장)
Redis 는 인메모리 기반이지만 필요에 따라 중요 데이터를 지속적으로 저장할 필요가 있는데 이럴 경우 디스크 저장 장치에 파일로 저장할 수 있다.
또한 Redis 서버를 재시작한 후 파일에 저장해 둔 데이터를 다시 메모리로 업로더할 수도 있다.
5.1. RDB (Redis DataBase) 파일을 이용하여 저장(=SAVE 명령어 이용)
SAVE 명령어를 이용하면 일정 주기마다 일정 개수의 key 데이터를 디스크 상의 dump.rdb 파일로 저장할 수 있다.
SAVE명령어에 대한 내용은 Redis 기본, 데이터 처리 명령어, String 의 2.6.SAVE를 참고하세요.
저장 주기와 저장 단위를 직접 결정할 수 있고 시스템 자원이 최소한으로 요구되고 복구 시간이 빠르며, 저장 공간이 압축되므로 별도의 파일 압축이 필요없다는 장점이 있지만, 데이터 최종 저장 후 새로운 저장이 수행되는 시점 전에 시스템 장애가 발생하는 경우 데이터 유실이 발생할 수 있다는 단점이 있다.
RDB 파일에는 SAVE 명령어를 실행한 시점에 메모리 상에 저장된 모든 데이터를 스냅샷 형태로 저장한다.
$ vi /usr/local/etc/redis.conf
...
save 60 1000 # 60초마다 1,000 개의 key 저장
$ pwd
/usr/local/var/db/redis
$ ll
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 assu admin 108B 7 21 15:10 dump.rdb
5.2. AOF (Append Only File) 명령어 이용하여 저장 (= bgrewriteaof 명령어 이용)
bgrewriteaof 명령어를 이용하면 디스크 상에 appendonly.aof 파일로 데이터를 저장할 수 있다.
명령어 실행 후에 입력/수정/삭제되는 모든 데이터를 저장한다.
지속적인 쓰기 작업이 발생하므로 시스템 자원이 집중적으로 요구되고, 마지막 시점까지 데이터 복구가 가능하다는 장점이 있지만,
대용량 데이터 파일로 복구 작업 시 복구 성능이 떨어지며 저장 공간이 압축되지 않는 단점이 있다.
$ vi /usr/local/etc/redis.conf
...
appendonly yes # AOF 환경 설정
appendonlyname "appendonly.aof" # AOF 파일명
6. Copy on Write
메모리 상에 로더된 데이터를 하나의 부모 프로세스가 참고하고 있는 도중에 자식 프로세스가 동시에 참조 관계를 가지게 되는 경우 서버 프로세스는 별도의 저장공간에 이를 복제하게 되는데 이를 Copy on Write 라고 한다.
Copy on Write 가 빈번하게 발생하면 해당 operation 은 지연되고, 이는 Redis 서버 전체의 성능 지연 문제로 이어지기 때문에 이러한 현상이 자주 발생하지 않도록 데이터를 처리하고 만일 발생했다 하더라도 지연 문제가 빨리 해소될 수 있도록 충분한 메모리를 확보하는 것이 중요하다.
Copy on Write가 발생하는 경우SAVE파라미터에 의해 주기적으로 RDB 파일 생성할 때SAVE명령어 또는 파라미터는 Redis WorkingSets 영역에 저장되어 있는 데이터를 디스크의 dump.rdb 파일로 저장할 때 사용되는데 이 때 Copy on Write 가 발생
BGSAVE명령어에 의해 RDB 파일을 저장할 때BGREWRITEAOF명령어에 의해 AOF 파일을 저장할 때SAVE,BGSAVE명령어가 dump.rdb 파일에 쓰기 작업을 하는 것이라면BGREWRITEAOF는 appendonly.aof 파일에 쓰기 작업을 하는 것으로 이 경우도 Copy on Write 가 발생
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage파라메티에 의해 AOF 파일을 재저장할 때- AOF 파일이 가득 채워진 상태에서 계속 데이터를 저장해야 하는 경우 AOF 파일을 비우고 처음부터 다시 write 작업을 수행하는 경우가 발생
- 성능 이슈가 발생하는 환경에서는 위 파라미터의 적극 사용은 권장하지 않음
Master-Slave,Partition-Replication서버 환경으로 구동 시- Master 서버의 데이터를 Slave 서버에 복제할 때 Copy on Write 발생
7. Benchmark For Redis
성능 이슈가 발생하는 경우 원인을 찾기 위해서는 실제 실행되고 있는 환경에서 수행되어야 하는데 동일한 시스템 환경을 임의로 만드는 것은 쉬운 일이 아니다.
Redis 서버는 redis-benchmark.exe 실행 코드를 제공하는데 이를 통해 실제와 같은 데이터를 임의로 발생시켜 성능 이슈가 발생할 수 있는 가상 상태를 만들어 성능 최적화 작업을 수행할 수 있다.
redis-benchmark [-h <host>] [-p <port>] [-c <clients>] [-n <requests>] [-k <boolean>]
8. 관리 명령어 (redis-cli)
info: redis server 현재 상태 확인select: redis server 내 생성되어 있는 db 로 switchdbsize: 현재 db 에 생성되어 있는 key 갯수swapdb: 현재 db 에 할당한 swapDB 생성flushall/flushdb: 현재 생성되어 있는 모든 keys 및 db 삭제client list: redis server 에 접속되어 있는 client 정보 조회client getname: client 명 조회client kill: 해당 client 제거time: redis server 현재 시간
info
> info
# Server
redis_version:7.0.4 # 설치 버전
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:ef6295796237ef48
redis_mode:standalone # standalone or cluster mode
os:Darwin 21.6.0 x86_64 # OS 버전
arch_bits:64
monotonic_clock:POSIX clock_gettime
multiplexing_api:kqueue
atomicvar_api:c11-builtin
gcc_version:4.2.1
process_id:7780
process_supervised:no
run_id:6917cb98103ea777c783cd115e6df13351080446
tcp_port:6379 # tcp-ip port
server_time_usec:1663545012394760
uptime_in_seconds:498149
uptime_in_days:5
hz:10
configured_hz:10
lru_clock:2600628
executable:/usr/local/opt/redis/bin/redis-server # 인스턴스 실행 코드
config_file:/usr/local/etc/redis.conf
io_threads_active:0
# Clients
connected_clients:1 # 접속된 client 수
cluster_connections:0
maxclients:10000
client_recent_max_input_buffer:16896
client_recent_max_output_buffer:0
blocked_clients:0
tracking_clients:0
clients_in_timeout_table:0
# Memory
used_memory:1798432 # 사용중인 메모리 크기
used_memory_human:1.72M
used_memory_rss:1490944
used_memory_rss_human:1.42M
used_memory_peak:3529952
used_memory_peak_human:3.37M
used_memory_peak_perc:50.95%
used_memory_overhead:1198760
used_memory_startup:1192144
used_memory_dataset:599672
used_memory_dataset_perc:98.91%
allocator_allocated:1779456
allocator_active:1459200
allocator_resident:1459200
total_system_memory:17179869184 # 사용 가능한 시스템 메모리 크기
total_system_memory_human:16.00G
used_memory_lua:31744
used_memory_vm_eval:31744
used_memory_lua_human:31.00K
used_memory_scripts_eval:0
number_of_cached_scripts:0
number_of_functions:0
number_of_libraries:0
used_memory_vm_functions:32768
used_memory_vm_total:64512
used_memory_vm_total_human:63.00K
used_memory_functions:216
used_memory_scripts:216
used_memory_scripts_human:216B
maxmemory:0 # redis 서버가 사용할 수 있는 최대 메모리 크기
maxmemory_human:0B
maxmemory_policy:noeviction
allocator_frag_ratio:0.82
allocator_frag_bytes:18446744073709231360
allocator_rss_ratio:1.00
allocator_rss_bytes:0
rss_overhead_ratio:1.02
rss_overhead_bytes:31744
mem_fragmentation_ratio:0.84 # redis 서버의 단편화 상태
mem_fragmentation_bytes:-288512
mem_not_counted_for_evict:0
mem_replication_backlog:0
mem_total_replication_buffers:0
mem_clients_slaves:0
mem_clients_normal:1776
mem_cluster_links:0
mem_aof_buffer:0
mem_allocator:libc
active_defrag_running:0
lazyfree_pending_objects:0
lazyfreed_objects:0
# Persistence
loading:0
async_loading:0
current_cow_peak:0
current_cow_size:0
current_cow_size_age:0
current_fork_perc:0.00
current_save_keys_processed:0
current_save_keys_total:0
rdb_changes_since_last_save:0
rdb_bgsave_in_progress:0
rdb_last_save_time:1663503752 # 마지막 저장 시간
rdb_last_bgsave_status:ok # 마지막 저장 상태
rdb_last_bgsave_time_sec:0
rdb_current_bgsave_time_sec:-1
rdb_saves:7
rdb_last_cow_size:0
rdb_last_load_keys_expired:0
rdb_last_load_keys_loaded:2
aof_enabled:0 # AOF 설정 상태
aof_rewrite_in_progress:0
aof_rewrite_scheduled:0
aof_last_rewrite_time_sec:-1
aof_current_rewrite_time_sec:-1
aof_last_bgrewrite_status:ok
aof_rewrites:0
aof_rewrites_consecutive_failures:0
aof_last_write_status:ok
aof_last_cow_size:0
module_fork_in_progress:0
module_fork_last_cow_size:0
# Stats
total_connections_received:6019
total_commands_processed:2565935
instantaneous_ops_per_sec:0
total_net_input_bytes:77268404
total_net_output_bytes:27488768
total_net_repl_input_bytes:0
total_net_repl_output_bytes:0
instantaneous_input_kbps:0.00
instantaneous_output_kbps:0.00
instantaneous_input_repl_kbps:0.00
instantaneous_output_repl_kbps:0.00
rejected_connections:0
sync_full:0
sync_partial_ok:0
sync_partial_err:0
expired_keys:0
expired_stale_perc:0.00
expired_time_cap_reached_count:0
expire_cycle_cpu_milliseconds:2407
evicted_keys:0
evicted_clients:0
total_eviction_exceeded_time:0
current_eviction_exceeded_time:0
keyspace_hits:1279705
keyspace_misses:52
pubsub_channels:0
pubsub_patterns:0
pubsubshard_channels:0
latest_fork_usec:632
total_forks:7
migrate_cached_sockets:0
slave_expires_tracked_keys:0
active_defrag_hits:0
active_defrag_misses:0
active_defrag_key_hits:0
active_defrag_key_misses:0
total_active_defrag_time:0
current_active_defrag_time:0
tracking_total_keys:0
tracking_total_items:0
tracking_total_prefixes:0
unexpected_error_replies:0
total_error_replies:4
dump_payload_sanitizations:0
total_reads_processed:28417
total_writes_processed:22406
io_threaded_reads_processed:0
io_threaded_writes_processed:0
reply_buffer_shrinks:37
reply_buffer_expands:87
# Replication
role:master # 서버 타입
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:d299b8c5912c1a59be5dd0ee1e34c7ba4d503178
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:0
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:0
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0
repl_backlog_histlen:0
# CPU
used_cpu_sys:70.667449 # 현재 사용중인 CPU 사용율
used_cpu_user:51.179344
used_cpu_sys_children:0.014831
used_cpu_user_children:0.003161
# Modules
module:name=ReJSON,ver=999999,api=1,filters=0,usedby=[],using=[],options=[handle-io-errors]
# Errorstats
errorstat_ERR:count=4
# Cluster
cluster_enabled:0 # 클러스터 모드 상태
# Keyspace # db 갯수 및 상태
db0:keys=90,expires=0,avg_ttl=0
8.1. 테스트
세션1
> info # 위 수치 참고
...
세션 2
$ redis-benchmark -q -n 1000000 # 1,000,000 데이터 입력 테스트
^CNG_INLINE: rps=63733.1 (overall: 68326.9) avg_msec=0.545 (overall: 0.500)
...
세션1
> info memory # 메모리 확인
# Memory
used_memory:2754160 # 전체 메모리 사용상태 증가 (기존: 1798432)
used_memory_human:2.63M
used_memory_rss:1880064
...
> info cpu # CPU 확인
# CPU
used_cpu_sys:82.501118 # CPU 사용율 증가 (기존: 70.667449)
used_cpu_user:58.178811
used_cpu_sys_children:0.014831
used_cpu_user_children:0.003161
...
> info keyspace
# Keyspace # 현재 활성화된 db명, 갯수, key 갯수
db0:keys=90,expires=0,avg_ttl=0
> select 0 # 0번 db
OK
> dbsize # 해당 db 에 저장된 key 갯수
(integer) 90
> select 1 # 1번 db
OK
> dbsize # 해당 db 에 저장된 key 갯수
(integer) 0
> exit
> client list # 현재 접속되어 있는 클라이언트 정보
id=6277 addr=127.0.0.1:65090 laddr=127.0.0.1:6379 fd=8 name= age=3 idle=0 flags=N db=0 sub=0 psub=0 ssub=0
multi=-1 qbuf=26 qbuf-free=16864 argv-mem=10 multi-mem=0 rbs=1024 rbp=0 obl=0 oll=0 omem=0 tot-mem=18682 events=r
cmd=client|list user=default redir=-1 resp=2
addr: the client address.fd: the client socket file descriptor number.name: the client name as set by CLIENT SETNAME.age: them number of seconds the connection existed for.idle: the number of seconds the connection is idle.flags: the kind of client (N: normal client)omem: the amount of memory used by the client for the output buffer.cmd: the last executed command.
서버 상태 모니터링
$ redis-cli --stat
------- data ------ --------------------- load -------------------- - child -
keys mem clients blocked requests connections
0 1.82M 1 0 6251247 (+0) 6326
0 1.81M 1 0 6251248 (+1) 6326
0 1.81M 1 0 6251249 (+1) 6326
0 3.45M 51 0 6281227 (+29978) 6377 # <-- redis-benchmark -q -n 1000000 입력 시점
0 3.11M 51 0 6344817 (+63590) 6377
0 2.73M 51 0 6409422 (+64605) 6377
0 2.73M 51 0 6470592 (+61170) 6377
0 2.73M 51 0 6531187 (+60595) 6377
0 2.73M 51 0 6592606 (+61419) 6377
0 2.73M 51 0 6652797 (+60191) 6377
0 1.81M 1 0 6663671 (+10874) 6377
0 1.81M 1 0 6663672 (+1) 6377
0 1.81M 1 0 6663673 (+1) 6377
9. Data Export, Import
Redis 에서 데이터를 디스크에 즉시 저장하지 않는 이유는 디스트 IO 로 인해 발생하는 성능 지연 문제를 피함으로써 성능 개선이 목적이다.
하지만 모든 데이터를 메모리에서 관리할 수만은 없는데 예기치 못한 원인으로 시스템이 종료되었을 경우 데이터가 유실될 수도 있고, 새로운 Redis 서버로 데이터를 이전해야 하는 경우가 발생할 수 있기 때문이다.
9.1. SAVE 명령어로 rdb file export & import
SAVE명령어는 위의 5.1. RDB 파일을 이용하여 저장(=SAVE명령어 이용) 를 참고하세요.
export
> hset jhtest hahaha 111
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "jhtest"
127.0.0.1:6379> save
$ pwd
/usr/local/var/db/redis
$ ll
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 - admin 119B 9 19 13:33 dump.rdb
import
$redis-cli --rdb /usr/local/var/db/redis/dump.rdb
sending REPLCONF capa eof
sending REPLCONF rdb-only 1
SYNC sent to master, writing bytes of bulk transfer until EOF marker to '/usr/local/var/db/redis/dump.rdb'
Transfer finished with success after 172 bytes
다른 포트로 Redis 서버를 띄우고 import or 기존에 뜬 서버에서 keys 삭제 후 import 후 keys * 실행 시 dump.rdb 파일대로 나오지 않음.. 왜일까…?
9.2. bgrewriteaof 명령어로 aof file export
bgrewriteaof명령어는 위의 5.2. AOF (Append Only File) 명령어 이용하여 저장 (=bgrewriteaof명령어 이용) 를 참고하세요.
$ redis-cli -n 1000 --pipe < appendonly.aof
9.3. scan 명령어로 text file export
$ redis-cli --csv --scan > 2022.csv
$ ll
total 520
-rw-r--r-- 1 - admin 11B 9 19 14:12 2022.csv
$ cat 2022.csv
───────┬─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ File: 2022.csv
───────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ jhtesttest
───────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
10. Redis Serialization Protocol & Mass Insertion
대량의 데이터를 Redis 클아이언트를 통해 Redis 서버로 저장해야하는 경우가 있다.
이 때 일반적인 Redis 명령어로 생성된 파일을 입력하게 되면, 클라이언트 레벨에서 작성된 텍스트 파일의 명령어는 네트워크를 통해 Redis 서버로 전성되어야 하고, 처리된 결과는 다시 클라이언트로 전달되는 방식이기 때문에 빠른 성능을 보장할 수 없다.
10.1. Luke Protocol 을 이용한 업로드
$ vi luke_data.dat
set 111 assu
set 222 assu2
$ redis-cli flushall
OK
$ cat luke_data.dat | redis-cli --pipe
All data transferred. Waiting for the last reply...
Last reply received from server.
errors: 0, replies: 2
$ redis-cli --scan
"111"
"222"
$ redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "111"
2) "222"
10.2. Request Response Protocol(RERP) 을 이용한 업로드
Luke Protocol 을 이용한 업로드의 단점은 업로드의 성능 지연문제인데 이를 해소한 것이 RERP (Redis Serialization Protocol) 방식이다.
11. redis-cli option
$ redis-cli --help
Usage: redis-cli [OPTIONS] [cmd [arg [arg ...]]]
-h <hostname> Server hostname (default: 127.0.0.1).
-p <port> Server port (default: 6379).
-s <socket> Server socket (overrides hostname and port).
-a <password> Password to use when connecting to the server.
You can also use the REDISCLI_AUTH environment
variable to pass this password more safely
(if both are used, this argument takes precedence).
--user <username> Used to send ACL style 'AUTH username pass'. Needs -a.
--pass <password> Alias of -a for consistency with the new --user option.
--askpass Force user to input password with mask from STDIN.
If this argument is used, '-a' and REDISCLI_AUTH
environment variable will be ignored.
-u <uri> Server URI.
-r <repeat> Execute specified command N times.
-i <interval> When -r is used, waits <interval> seconds per command.
It is possible to specify sub-second times like -i 0.1.
This interval is also used in --scan and --stat per cycle.
and in --bigkeys, --memkeys, and --hotkeys per 100 cycles.
-n <db> Database number.
-2 Start session in RESP2 protocol mode.
-3 Start session in RESP3 protocol mode.
-x Read last argument from STDIN (see example below).
-X Read <tag> argument from STDIN (see example below).
-d <delimiter> Delimiter between response bulks for raw formatting (default: \n).
-D <delimiter> Delimiter between responses for raw formatting (default: \n).
-c Enable cluster mode (follow -ASK and -MOVED redirections).
-e Return exit error code when command execution fails.
--tls Establish a secure TLS connection.
--sni <host> Server name indication for TLS.
--cacert <file> CA Certificate file to verify with.
--cacertdir <dir> Directory where trusted CA certificates are stored.
If neither cacert nor cacertdir are specified, the default
system-wide trusted root certs configuration will apply.
--insecure Allow insecure TLS connection by skipping cert validation.
--cert <file> Client certificate to authenticate with.
--key <file> Private key file to authenticate with.
--tls-ciphers <list> Sets the list of preferred ciphers (TLSv1.2 and below)
in order of preference from highest to lowest separated by colon (":").
See the ciphers(1ssl) manpage for more information about the syntax of this string.
--tls-ciphersuites <list> Sets the list of preferred ciphersuites (TLSv1.3)
in order of preference from highest to lowest separated by colon (":").
See the ciphers(1ssl) manpage for more information about the syntax of this string,
and specifically for TLSv1.3 ciphersuites.
--raw Use raw formatting for replies (default when STDOUT is
not a tty).
--no-raw Force formatted output even when STDOUT is not a tty.
--quoted-input Force input to be handled as quoted strings.
--csv Output in CSV format.
--json Output in JSON format (default RESP3, use -2 if you want to use with RESP2).
--quoted-json Same as --json, but produce ASCII-safe quoted strings, not Unicode.
--show-pushes <yn> Whether to print RESP3 PUSH messages. Enabled by default when
STDOUT is a tty but can be overridden with --show-pushes no.
--stat Print rolling stats about server: mem, clients, ...
--latency Enter a special mode continuously sampling latency.
If you use this mode in an interactive session it runs
forever displaying real-time stats. Otherwise if --raw or
--csv is specified, or if you redirect the output to a non
TTY, it samples the latency for 1 second (you can use
-i to change the interval), then produces a single output
and exits.
--latency-history Like --latency but tracking latency changes over time.
Default time interval is 15 sec. Change it using -i.
--latency-dist Shows latency as a spectrum, requires xterm 256 colors.
Default time interval is 1 sec. Change it using -i.
--lru-test <keys> Simulate a cache workload with an 80-20 distribution.
--replica Simulate a replica showing commands received from the master.
--rdb <filename> Transfer an RDB dump from remote server to local file.
Use filename of "-" to write to stdout.
--functions-rdb <filename> Like --rdb but only get the functions (not the keys)
when getting the RDB dump file.
--pipe Transfer raw Redis protocol from stdin to server.
--pipe-timeout <n> In --pipe mode, abort with error if after sending all data.
no reply is received within <n> seconds.
Default timeout: 30. Use 0 to wait forever.
--bigkeys Sample Redis keys looking for keys with many elements (complexity).
--memkeys Sample Redis keys looking for keys consuming a lot of memory.
--memkeys-samples <n> Sample Redis keys looking for keys consuming a lot of memory.
And define number of key elements to sample
--hotkeys Sample Redis keys looking for hot keys.
only works when maxmemory-policy is *lfu.
--scan List all keys using the SCAN command.
--pattern <pat> Keys pattern when using the --scan, --bigkeys or --hotkeys
options (default: *).
--quoted-pattern <pat> Same as --pattern, but the specified string can be
quoted, in order to pass an otherwise non binary-safe string.
--intrinsic-latency <sec> Run a test to measure intrinsic system latency.
The test will run for the specified amount of seconds.
--eval <file> Send an EVAL command using the Lua script at <file>.
--ldb Used with --eval enable the Redis Lua debugger.
--ldb-sync-mode Like --ldb but uses the synchronous Lua debugger, in
this mode the server is blocked and script changes are
not rolled back from the server memory.
--cluster <command> [args...] [opts...]
Cluster Manager command and arguments (see below).
--verbose Verbose mode.
--no-auth-warning Don't show warning message when using password on command
line interface.
--help Output this help and exit.
--version Output version and exit.
Cluster Manager Commands:
Use --cluster help to list all available cluster manager commands.
Examples:
cat /etc/passwd | redis-cli -x set mypasswd
redis-cli -D "" --raw dump key > key.dump && redis-cli -X dump_tag restore key2 0 dump_tag replace < key.dump
redis-cli -r 100 lpush mylist x
redis-cli -r 100 -i 1 info | grep used_memory_human:
redis-cli --quoted-input set '"null-\x00-separated"' value
redis-cli --eval myscript.lua key1 key2 , arg1 arg2 arg3
redis-cli --scan --pattern '*:12345*'
참고 사이트 & 함께 보면 좋은 사이트
본 포스트는 주종면 저자의 빅데이터 저장 및 분석을 위한 NoSQL & Redis를 기반으로 스터디하며 정리한 내용들입니다.
- 빅데이터 저장 및 분석을 위한 NoSQL & Redis
- 빅데이터 저장 및 분석을 위한 NoSQL & Redis - 실습파일
- 센티넬이란, 센티넬 구동 및 모니터링 방법
- redis.io - eviction
- redis-cli option
