NestJS - Database, TypeORM
in DEV on Javascript, Nestjs, Typeorm
이 포스트는 NestJS 에 MySQL 과 TypeORM 을 적용해보는 법에 대해 알아본다.
소스는 user-service 에 있습니다.
1. MySQL 설정
NestJS 는 TypeORM, MikroORM, Sequelize, Knex.js, Prisma 와 같은 ORM 을 지원한다.
이 포스트에선 MySQL 와 TypeORM 을 이용할 예정이다.
docker 를 이용하여 mysql 을 실행하는 방법은 Rancher Desktop (Docker Desktop 유료화 대응) 을 참고하세요.
TypeORM 와 Sequelize 비교글은 Typescript - TypeORM vs Sequelize 을 참고하세요.
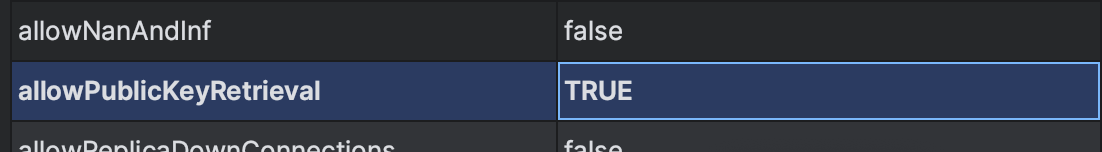
MySQL 8.0 부터는 설정에서 Public Key 등록을 허용해주어야 한다.
MySQL 설정이 끝났으면 test DB 를 하나 만든다.
한글 정렬이 잘 되도록 하기 위해 Charset 은 utf8mb4, Collation 은 utf8mb4_unicode_ci 로 설정한다.
create database test default charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
2. 유저 서비스
2.1. TypeORM 으로 DB 연결
NestJS 에 MySQL 연결을 위한 라이브러리를 설치한다.
$ npm i typeorm@0.3.12 @nestjs/typeorm@9.0.1 mysql2@3.2.0
app.module.ts
import { TypeOrmModule } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
@Module({
imports: [
UsersModule,
ConfigModule.forRoot({
envFilePath: [`${__dirname}/config/env/.${process.env.NODE_ENV}.env`],
load: [emailConfig], // ConfigFactory 지정
isGlobal: true, // 전역으로 등록해서 어느 모듈에서나 사용 가능
validationSchema, // 환경 변수 값에 대해 유효성 검사 수행
}),
//TypeORMModule 을 동적으로 가져옴
TypeOrmModule.forRoot({
type: 'mysql',
host: 'localhost',
port: 3306,
username: 'root',
password: 'test',
database: 'test',
entities: [__dirname + '/**/*.entity{.ts,.js}'], // TypeORM 이 구동될 때 인식하도록 할 entity 클래스의 경로 지정
synchronize: true, // 서비스 구동 시 소스 코드 기반으로 DB 스키마 동기화할지 여부, PROD 에서는 false 로 할 것
}),
],
controllers: [],
providers: [],
})
export class AppModule {}
syncronize옵션을 true 로 지정 시 서비스가 실행되서 DB 연결 시 DB 가 초기화되므로 PROD 에서는 절대 true 로 지정하면 안된다.
TypeOrmModule.forRoot 의 시그니처
static forRoot(options?: TypeOrmModuleOptions): DynamicModule;
TypeOrmModuleOptions 의 시그니처
export declare type TypeOrmModuleOptions = {
/**
* Number of times to retry connecting
* Default: 10
*/
retryAttempts?: number;
/**
* Delay between connection retry attempts (ms)
* Default: 3000
*/
retryDelay?: number;
/**
* Function that determines whether the module should
* attempt to connect upon failure.
*
* @param err error that was thrown
* @returns whether to retry connection or not
*/
toRetry?: (err: any) => boolean;
/**
* If `true`, entities will be loaded automatically.
*/
autoLoadEntities?: boolean;
/**
* If `true`, connection will not be closed on application shutdown.
* @deprecated
*/
keepConnectionAlive?: boolean;
/**
* If `true`, will show verbose error messages on each connection retry.
*/
verboseRetryLog?: boolean;
} & Partial<DataSourceOptions>;
retryAttempts- 연결 시 재시도 횟수, default 10
retryDelay- 재시도 간 지연시간, ms 단위이며 default 3000
toRetry- 에러 발생 시 연결을 시도할 지 판단하는 함수
- 콜백으로 받은 인수 err 을 이용하여 연결 여부를 판단하는 함수를 구현하면 됨
autoLoadEntities- entity 를 자동으로 로드할 지 여부
keepConnectionAlive- 애플리케이션 종료 후 연결을 유지할 지 여부
verboseRetryLog- 연결 재시도 시 verbose 레벨로 에러 메시지를 보여줄 지 여부
TypeOrmModuleOptions 은 DataSourceOptions 타입의 Partial 타입을 교차(&) 한 타입이다.
Partial 제네릭 타입은 선언한 타입의 일부 속성만을 가질 수 있도록 하는 타입이고, 교차 타입은 교차시킨 타입의 속성들을 모두 갖는 타입이다.
위에서 설정한 옵션 외 다른 옵션을 조정하려면 DataSourceOptions 중 MysqlConnectionOptions 을 보고 설정하면 된다.
이제 위에서 host, username, password 등과 같은 예민한 정보를 환경 변수에서 읽어오도록 수정한다.
TypeOrmModule.forRoot({
type: 'mysql',
host: process.env.DATABASE_HOST,
port: 3306,
username: process.env.DATABASE_USERNAME,
password: process.env.DATABASE_PASSWORD,
database: 'test',
entities: [__dirname + '/**/*.entity{.ts,.js}'], // TypeORM 이 구동될 때 인식하도록 할 entity 클래스의 경로 지정
synchronize: true, // 서비스 구동 시 소스 코드 기반으로 DB 스키마 동기화할지 여부, PROD 에서는 false 로 할 것
}),
ormconfig.json 방식도 있는데 이 방식은 typeorm 0.3 버전에서는 지원하지 않는다. (0.2.x 버전까지만 지원)
2.2. 회원 가입 시 유저 정보 저장: @InjectRepository
NestJS 는 리포지터리 패턴 을 지원한다.
유저 Entity 를 정의한다.
/src/users/entity/user.entity.ts
import { Column, Entity, PrimaryColumn } from 'typeorm';
@Entity('User')
export class UserEntity {
@PrimaryColumn()
id: string;
@Column({ length: 30 })
name: string;
@Column({ length: 60 })
email: string;
@Column({ length: 30 })
password: string;
@Column({ length: 60 })
signupVerifyToken: string;
}
이제 이 유저 Entity 를 DB 에서 사용할 수 있도록 TypeOrmModuleOptions 의 entities 속성의 값으로 넣어준다.
TypeOrmModule.forRoot({
...
entities: [UserEntity], // TypeORM 이 구동될 때 인식하도록 할 entity 클래스의 경로 지정
...
}),
하지만 처음에 이미 dist 디렉터리 내의 .entity.ts 또는 .entity.js 로 끝나는 파일을 참조하도록 해두었으므로 수정하지 않아도 된다.
entities: [__dirname + '/**/*.entity{.ts,.js}'], // TypeORM 이 구동될 때 인식하도록 할 entity 클래스의 경로 지정
이제 서비스를 구동하면 User 테이블이 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다. (synchronize 옵션이 true 이므로)
CREATE TABLE `User` (
`id` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(60) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`signupVerifyToken` varchar(60) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci
이제 NestJS - Provider 의 2.2. 회원 가입 에서 TODO 로 남겨둔 작업들을 구현해본다.
UsersModule 에 forFeature() 로 유저 모듈 내에서 사용할 저장소 등록
/src/users/users.module.ts
import { TypeOrmModule } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
import { UserEntity } from './entity/user.entity';
@Module({
imports: [EmailModule,
TypeOrmModule.forFeature([UserEntity])], // UsersModule 에 forFeature() 로 유저 모듈 내에서 사용할 저장소 등록
controllers: [UsersController],
providers: [UsersService],
})
export class UsersModule {}
UsersService 에 @InjectRepository 데커레이터로 유저 저장소 주입
/src/users/users.service.ts
import { InjectRepository } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
import { UserEntity } from './entity/user.entity';
import { Repository } from 'typeorm';
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
constructor(
private emailService: EmailService,
//UsersService 에 `@InjectRepository` 데커레이터로 유저 저장소 주입
@InjectRepository(UserEntity)
private userRepository: Repository<UserEntity>,
) { }
...
}
유저 정보 저장 (saveUser)
import { ulid } from 'ulid';
...
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
...
// 유저 정보 저장
private async saveUser(
name: string,
email: string,
password: string,
signupVerifyToken: string,
) {
const user = new UserEntity(); // 유저 엔티티 객체 생성
user.id = ulid();
user.name = name;
user.email = email;
user.password = password;
user.signupVerifyToken = signupVerifyToken;
await this.userRepository.save(user);
}
}
ulid 는 ULID vs UUID: Sortable Random ID Generators for JavaScript 을 참고하세요.
이제 유저 생성 API 를 호출하면 DB 에 유저 정보가 저장되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
$ curl --location 'http://localhost:3000/users' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"name": "assu",
"email": "assu@test.com",
"password": "12341234"
}' | jq
가입 유무 확인 (checkUserExists)
// 가입 유무 확인
private async checkUserExists(email: string) {
const user = await this.userRepository.findOne({
where: { email: email },
});
return user !== null;
}
유저 생성 시 이메일이 존재하면 422 리턴
// 회원 가입
async createUser(name: string, email: string, password: string)
{
// 가입 유무 확인
const userExist = await this.checkUserExists(email);
if (userExist) {
throw new UnprocessableEntityException('Email already exists');
}
...
}
$ curl --location 'http://localhost:3000/users' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"name": "assu",
"email": "assu@test.com",
"password": "12341234"
}' | jq
{
"statusCode": 422,
"message": "Email already exists",
"error": "Unprocessable Entity"
}
2.3. Transaction 적용
TypeORM 에서 Transaction 을 처리하는 방법은 2가지가 있다.
- QueryRunner 로 적용
- transaction 함수 직접 사용하여 적용
2.3.1. QueryRunner 로 적용
TypeORM 에서 제공하는 DataSource 객체 주입
/src/users/users.service.ts
import { DataSource, Repository } from 'typeorm';
@Injectable()
export class UsersService {
...
constructor(
private dataSource: DataSource, // TypeORM 에서 제공하는 DataSource 객체 주입
) { }
...
}
위처럼 DataSource 객체를 주입하고 나면 DataSource 객체에서 트랜잭션을 생성할 수 있다.
// 유저 정보 저장 - QueryRunner 로 트랜잭션 제어
private async saveUserUsingQueryRunner(
name: string,
email: string,
password: string,
signupVerifyToken: string,
) {
// 주입받은 DataSource 객체에서 QueryRunner 생성
const queryRunner = this.dataSource.createQueryRunner();
// QueryRunner 에 DB 연결 후 트랜잭션 시작
await queryRunner.connect();
await queryRunner.startTransaction();
try {
const user = new UserEntity(); // 유저 엔티티 객체 생성
user.id = ulid();
user.name = name;
user.email = email;
user.password = password;
user.signupVerifyToken = signupVerifyToken;
// 트랜잭션을 커밋하여 영속화(persistence) 함
await queryRunner.manager.save(user);
// 일부러 에러 발생 시 데이터 저장 안됨
// throw new InternalServerErrorException();
// DB 작업 수행 수 커밋하여 영속화 완료
await queryRunner.commitTransaction();
} catch (e) {
// 에러 발생 시 롤백
await queryRunner.rollbackTransaction();
} finally {
// 직접 생성한 QueryRunner 해제
await queryRunner.release();
}
}
2.3.2. transaction 함수 직접 사용하여 적용
dataSource 객체 내의 transaction 함수를 바료 이용할 수도 있다.
// 유저 정보 저장 - transaction 함수 직접 이용하여 트랜잭션 제어
private async saveUserUsingTransaction(
name: string,
email: string,
password: string,
signupVerifyToken: string,
) {
await this.dataSource.transaction(async (manager) => {
const user = new UserEntity(); // 유저 엔티티 객체 생성
user.id = ulid();
user.name = name;
user.email = email;
user.password = password;
user.signupVerifyToken = signupVerifyToken;
await manager.save(user);
// 일부러 에러 발생 시 데이터 저장 안됨
//throw new InternalServerErrorException();
});
}
2.4. 마이그레이션
TypeORM 을 이용하면 아래와 같은 장점이 있다.
- 마이그레이션을 위한 SQL 문을 직접 작성하지 않아도 됨
- 마이그레이션 롤백 작업도 간단한 명령어로 수행 가능
- 마이그레이션 코드를 일정한 형식으로 소스 저장소에서 관리 가능 (= DB 변경점을 소스 코드로 관리 가능)
- 마이그레이션 이력 관리 가능
- 특정 테이블에 마이그레이션 기록
- 필요 시 처음부터 다시 수행 가능
2.4.1. 마이그레이션을 CLI 로 생성하고 실행할 수 있는 환경 구성
migration cli 로 명령어를 수행하는데 필요한 패키지를 설치한다. typeorm cli 는 이미 설치한 typeorm 패키지에 포함되어 있다. typeorm cli 는 타입스크립트로 된 엔티티 파일을 읽어들이므로 typeorm cli 를 실행하기 위해 ts-node 패키지를 글로벌 환경으로 설치한다.
$ npm i -g ts-node
이제 ts-node 를 이용하여 npm run typeorm 명령어로 typeorm cli 를 실행할 수 있도록 package.json 을 수정한다.
"scripts": {
...
"typeorm-create": "ts-node -r ts-node/register ./node_modules/typeorm/cli.js",
"typeorm-generate": "ts-node -r tsconfig-paths/register ./node_modules/typeorm/cli.js -d ormconfig.ts"
...
}
ormconfig.ts 파일을 루트 디렉터리에 생성한다.
import { DataSource } from 'typeorm';
export const AppDataSource = new DataSource({
type: 'mysql',
host: '127.0.0.1',
//host: process.env.DATABASE_HOST,
port: 13306,
username: 'root',
//username: process.env.DATABASE_USERNAME,
password: ' ㅅㄷㄴㅅ',
//password: process.env.DATABASE_PASSWORD,
database: 'test',
entities: [__dirname + '/**/*.entity{.ts,.js}'],
synchronize: false,
migrations: [__dirname + '/dist/migrations/**/*{.ts,.js}'], // /dist/migrations 에 있는 파일 실행
migrationsTableName: 'migrations',
});
각 항목을 환경 변수 값으로 읽어오도록 하면 ormconfig.ts 파일이 ConfigModule.forRoot 로 환경 변수를 읽어오기 전에 컴파일이 되기 때문에 서버 구동에서 에러가 발생한다. 따라서 tsconfig.json 에서 컴파일 대상 소스를 아래와 같이 지정해준다.
"include": [
"src/**/*"
]
이제 마이그레이션 이력을 관리할 테이블을 설정한다.
/src/app.module.ts
//TypeORMModule 을 동적으로 가져옴
TypeOrmModule.forRoot({
...
synchronize: process.env.DATABASE_SYNCRONIZE === 'true', // 서비스 구동 시 소스 코드 기반으로 DB 스키마 동기화할지 여부, PROD 에서는 false 로 할 것
migrationsRun: false, // 서버가 구동될 때 작성된 마이그레이션 파일을 기반으로 마이그레이션 수행할 지 여부 설정, false 로 하여 cli 명령어로 직접 입력하도록 함
migrations: [__dirname + '/migrations/**/*{.ts,.js}'], // 마이그레이션을 수행할 파일이 관리되는 경로, 디폴트 migrations
migrationsTableName: 'migrations',
}),
이제 User 테이블 삭제 후 서버를 재기동한다.
2.4.2. 마이그레이션 실행
마이그레이션 파일 생성 방법은 2가지가 있다.
migration:create- 비어있는 파일 생성
migration:generate- 현재 소스 코드와 migrations 테이블에 기록된 이력을 기반으로 마이그레이션 파일 자동 생성
migration:create 로 마이그레이션 파일을 생성해본다.
$ npm run typeorm-create migration:create src/migrations/CreateUserTable
/src/migrations/1680768213491-CreateUserTable.ts
import { MigrationInterface, QueryRunner } from 'typeorm';
export class CreateUserTable1680768213491 implements MigrationInterface {
// migration:run 명령으로 마이그레이션이 수행될 때 수행될 코드
public async up(queryRunner: QueryRunner): Promise<void> {}
// migration:revert 명령으로 마이그레이션을 되돌릴 때 수행될 코드
public async down(queryRunner: QueryRunner): Promise<void> {}
}
위 파일을 삭제하고 migration:generate 로 다시 생성해본다.
$ npm run typeorm-generate migration:generate src/migrations/CreateUserTable
/src/migrations/1680768830565-CreateUserTable.ts
import { MigrationInterface, QueryRunner } from 'typeorm';
export class CreateUserTable1680768830565 implements MigrationInterface {
name = 'CreateUserTable1680768830565';
public async up(queryRunner: QueryRunner): Promise<void> {
await queryRunner.query(
`CREATE TABLE \`User\` (\`id\` varchar(255) NOT NULL, \`name\` varchar(30) NOT NULL, \`email\` varchar(60) NOT NULL, \`password\` varchar(30) NOT NULL, \`signupVerifyToken\` varchar(60) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (\`id\`)) ENGINE=InnoDB`,
);
}
public async down(queryRunner: QueryRunner): Promise<void> {
await queryRunner.query(`DROP TABLE \`User\``);
}
}
이제 migration:run 으로 마이그레이션을 수행해본다.
$ npm run typeorm-generate migration:run
> user-service@0.0.1 typeorm-generate
> ts-node -r tsconfig-paths/register ./node_modules/typeorm/cli.js -d ormconfig.ts migration:run
query: SELECT VERSION() AS `version`
query: SELECT * FROM `INFORMATION_SCHEMA`.`COLUMNS` WHERE `TABLE_SCHEMA` = 'test' AND `TABLE_NAME` = 'migrations'
query: SELECT * FROM `test`.`migrations` `migrations` ORDER BY `id` DESC
0 migrations are already loaded in the database.
1 migrations were found in the source code.
1 migrations are new migrations must be executed.
query: START TRANSACTION
query: CREATE TABLE `User` (`id` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `email` varchar(60) NOT NULL, `password` varchar(30) NOT NULL, `signupVerifyToken` varchar(60) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB
query: INSERT INTO `test`.`migrations`(`timestamp`, `name`) VALUES (?, ?) -- PARAMETERS: [1680769589673,"CreateUserTable1680769589673"]
Migration CreateUserTable1680769589673 has been executed successfully.
query: COMMIT
이제 migrate:revert 로 마이그레이션을 되돌려본다.
$ npm run typeorm-generate migration:revert
> user-service@0.0.1 typeorm-generate
> ts-node -r tsconfig-paths/register ./node_modules/typeorm/cli.js -d ormconfig.ts migration:revert
query: SELECT VERSION() AS `version`
query: SELECT * FROM `INFORMATION_SCHEMA`.`COLUMNS` WHERE `TABLE_SCHEMA` = 'test' AND `TABLE_NAME` = 'migrations'
query: SELECT * FROM `test`.`migrations` `migrations` ORDER BY `id` DESC
1 migrations are already loaded in the database.
CreateUserTable1680769589673 is the last executed migration. It was executed on Thu Apr 06 2023 17:26:29 GMT+0900 (Korean Standard Time).
Now reverting it...
query: START TRANSACTION
query: DROP TABLE `User`
query: DELETE FROM `test`.`migrations` WHERE `timestamp` = ? AND `name` = ? -- PARAMETERS: [1680769589673,"CreateUserTable1680769589673"]
Migration CreateUserTable1680769589673 has been reverted successfully.
query: COMMIT
참고 사이트 & 함께 보면 좋은 사이트
본 포스트는 한용재 저자의 NestJS로 배우는 백엔드 프로그래밍을 기반으로 스터디하며 정리한 내용들입니다.
- NestJS로 배우는 백엔드 프로그래밍
- NestJS로 배우는 백엔드 프로그래밍 - Github
- NestJS 공식문서
- NestJS docs
- Nest.js Github
- NestJS 공식 예제 Starter 프로젝트 Github
- docker mysql
- TypeORM vs Sequelize
- Rancher Desktop (Docker Desktop 유료화 대응)
- 리포지터리 패턴
- ULID vs UUID: Sortable Random ID Generators for JavaScript
- TypeORM Transaction
- Sequelize migration