Spring Security - 인증 구현(2): SecurityContext
in DEV on SpringSecurity, Security-context, Security-context-holder
이 포스트에서는 SecurityContext 를 관리하는 전략에 대해 알아본다.
소스는 github 에 있습니다.
목차
- 1.
SecurityContext,SecurityContextHolder- 1.1.
SecurityContext를 위한 보유 전략:MODE_THREADLOCAL - 1.2. 비동기 호출을 위한 보유 전략:
MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL - 1.3. 독립형 애플리케이션을 위한 보유전략:
MODE_GLOBAL - 1.4.
DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable로SecurityContext전달 - 1.5.
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService로SecurityContext전달 - 1.6.
SecurityContext를 별도의 스레드로 전파하는 객체들
- 1.1.
- 참고 사이트 & 함께 보면 좋은 사이트
개발 환경
- 언어: java
- Spring Boot ver: 3.2.2
- Spring ver: 6.1.3
- Spring Security ver: 6.2.1
- IDE: intelliJ
- SDK: JDK 17
- 의존성 관리툴: Maven
1. SecurityContext, SecurityContextHolder
여기서는 SecurityContext 의 작동 방식과 데이터 접근 방법에 대해 알아본 후 다양한 스레드 관련 시나리오에서 데이터를 관리하는 방법에 대해 알아본다.
그러고나면 다양한 상황에 대한 SecurityContext 를 구성할 수 있을 것이다.
여기서 앞으로 볼 내용을 이용하여 권한 부여를 구성할 때 SecurityContext 에 저장된 인증된 사용자에 대한 세부 정보를 사용할 수 있다.
권한 부여에 대한 상세한 내용은
Spring Security - 권한 부여(1): 권한과 역할에 따른 액세스 제한,
Spring Security - 권한 부여(2): 경로, HTTP Method 에 따른 엑세스 제한,
Spring Security - 필터 를 참고하세요.
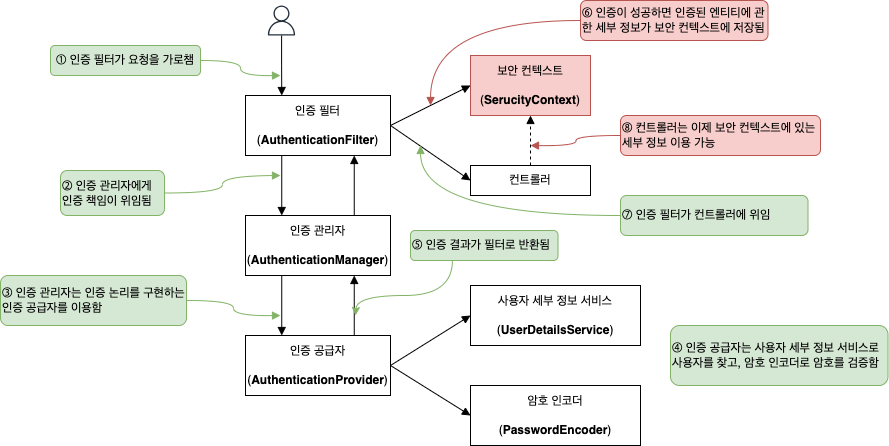
AuthenticationManager 는 인증 프로세스를 완료한 후 요청이 유지되는 동안 Authentication 인스턴스를 저장하는데, 이 Authentication 객체를 저장하는 인스턴스를 SecurityContext 라고 한다.
SecurityContext 인터페이스
package org.springframework.security.core.context;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
public interface SecurityContext extends Serializable {
Authentication getAuthentication();
void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication);
}
위에서 보듯이 SecurityContext 의 주된 책임은 Authentication 객체를 저장하는 것이다.
스프링 시큐리티는 SecurityContextHolder 객체를 통하여 SecurityContext 를 관리한다.
SecurityContextHolder 가 SecurityContext 를 관리하는 전략은 3가지가 있다.
MODE_THREADLOCAL- 각 스레드가
SecurityContext에 각자의 세부 정보를 저장 - 요청 당 스레드 방식의 웹 애플리케이션에서는 각 요청이 개별 스레드를 가지므로 가장 일반적인 접근법임
- 각 스레드가
MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCALMODE_THREADLOCAL과 비슷하지만 비동기 메서드의 경우SecurityContext를 다음 스레드로 복사하도록 스프링 시큐리티에 지시함- 이 방식으로
@Async메서드를 실행하는 새 스레드가SecurityContext를 상속하게 할 수 있음
MODE_GLOBAL- 애플리케이션의 모든 스레드가 같은
SecurityContext인스턴스를 바라봄
- 애플리케이션의 모든 스레드가 같은
SecurityContext 를 관리하는 스프링 시큐리티의 3가지 전략 외에도 개발자가 스프링에 알려지지 않은 스레드를 정의할 수 있는데 이럴 경우 SecurityContext 의 세부 정보를 명시적으로 새로운 스레드로 복사해야 한다.
이 부분은 바로 뒤인 1.4.
DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable로SecurityContext전달, 1.5.DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService로SecurityContext전달에 나옵니다.
1.1. SecurityContext 를 위한 보유 전략: MODE_THREADLOCAL
SecurityContext 를 관리하는 첫 번째 전략은 MODE_THREADLOCAL 로, 스프링 시큐리티가 SecurityContext 를 관리하는 기본 전략이기도 하다.
기본 전략인만큼 대부분 이 전략으로 충분하다.
MODE_THREADLOCAL 에서 스프링 시큐리티는 ThreadLocal(JDK 에 있는 구현) 을 이용하여 컨텍스트를 관리한다.
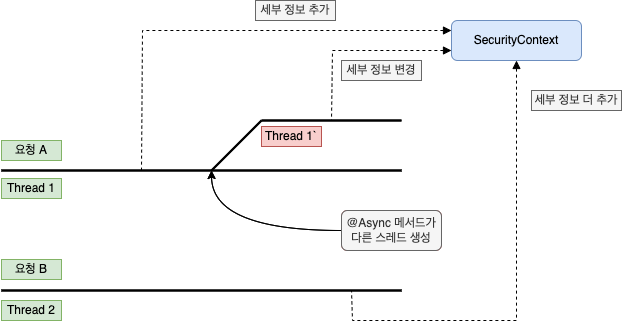
MODE_THREADLOCAL 으로 각 요청은 자신의 SecurityContext 에만 접근할 수 있으며 다른 스레드의 ThreadLocal 에는 접근할 수 없다.
즉, 각 요청은 자신의 SecurityContext 만 볼 수 있다는 의미이며 백엔드 웹 애플리케이션의 일반적인 작동 방식이다.
이렇게 MODE_THREADLOCAL 는 각 스레드의 SecurityContext 를 격리할 수 있게 해준다.
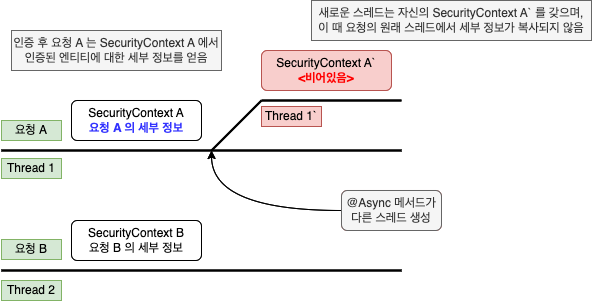
위 그림처럼 비동기 메서드가 호출되어 새로운 스레드가 생성되면 새로운 스레드도 자체적인 SecurityContext 를 가지며, 상위 스레드인 요청의 원래 스레더의 세부 정보가 새로운 스레드의 SecurityContext 에 복사되지 않는다.
MODE_THREADLOCAL 는 기본 전략이기 때문에 명시적으로 구성할 필요없이 인증 프로세스가 끝난 후 필요할 때마다 정적 getContext() 메서드로 SecurityContext 정보를 조회할 수 있다. SecurityContext 를 얻고 나면 여기에 저장된 엔티티의 세부 정보를 저장하는 Authentication 객체도 얻을 수 있다.
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
// SecurityContext 조회
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
// 인증된 정보 조회
Authentication authentication = securityContext.getAuthentication();
String name = authentication.getName();
스프링은 인증을 메서드 매개 변수로 바로 주입할 수 있으므로 엔드포인트 수준에서 위 방법말고 좀 더 편하게 컨텍스트 인증을 얻을 수 있다.
엔드포인트에서 인증 정보(Authentication) 조회
@GetMapping("hello")
public void hello(Authentication authentication) {
System.out.println(authentication.getName());
}
# 정상 호출
$ curl -w "%{http_code}" -u user:2a8f40ea-5c73-41ac-af7f-a9f867165445 http://localhost:8080/hello
user200%
# 인증없이 호출
$ curl -w "%{http_code}" -u assu:12345 http://localhost:8080/hello
401%
1.2. 비동기 호출을 위한 보유 전략: MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL
요청 당 여러 스레드가 사용될 때는 MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 전략을 사용한다.
먼저 MODE_THREADLOCAL 로 비동기 메서드가 실행될 때를 보자.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync // @Async 애너테이션 기능 활성화
public class ProjectConfig {
// ...
}
@EnableAsync 와 같은 구성 애너테이션을 가끔 메인 클래스(부트스트랩 클래스) 위에 지정하는 경우가 있는데 이럴 경우 기술적으로는 문제가 없지만 실제 애플리케이션은 책임을 분리하는 것을 선호하기 때문에 메인 클래스를 구성 클래스로 이용하는 것은 바람직하지 않다.
위 코드처럼 구성 애너테이션은 구성 클래스에 설정하는 것이 좋다.
@GetMapping("hello2")
@Async
public void hello2() {
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
String name = securityContext.getAuthentication().getName(); // NPE 발생
System.out.println(name);
}
위 코드를 실행하면 인증에서 이름을 얻는 곳에서 NPE 가 발생한다.
Stirng name = securityContext.getAuthentication().getName(); // NPE 발생
java.lang.NullPointerException: Cannot invoke "org.springframework.security.core.Authentication.getName()" because the return value of "org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext.getAuthentication()" is null
메서드가 SecurityContext 를 상속하지 않은 다른 스레드에서 실행되기 때문에 Authentication 객체가 null 이기 때문이다.
이럴 때 바로 MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 전략을 사용하면 된다.
MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 전략을 설정하면 프레임워크는 요청의 원래 스레드에 있는 인증 세부 정보를 비동기 메서드의 새로 생성된 스레드로 복사한다.
MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 전략 설정은 SecurityContextHolder.setStrategyName() 을 통해서 하거나, spring.security.strategy 시스템 속성을 이용하여 설정 가능하다.
아래는 SecurityContextHolder.setStrategyName() 메서드를 통해 SecurityContext 관리 전략을 설정하는 예시이다.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync // @Async 애너테이션 기능 활성화
public class ProjectConfig {
@Bean
public InitializingBean initializingBean() {
return () -> SecurityContextHolder.setStrategyName(SecurityContextHolder.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL);
}
}
$ curl -w "%{http_code}" -u user:ef361a2e-ce13-427c-9c61-32be21fd6079 http://localhost:8080/hello2
200%
<MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 전략 사용 시 주의점>
이 방식은 @Async 처럼 프레임워크가 자체적으로 스레드를 만들 때만 작동한다.
만일 코드로 직접 스레드를 만들면 프레임워크가 코드에서 생성한 스레드에 대해 모르기 때문에 MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 전략을 활성화해도 새로운 스레드로 인증 정보가 복사되지 않는다.
이럴 경우에 대한 방안은 1.4. DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 로 SecurityContext 전달, 1.5. DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService 로 SecurityContext 전달 에 나온다.
1.3. 독립형 애플리케이션을 위한 보유전략: MODE_GLOBAL
SecurityContext 가 애플리케이션의 모든 스레드에 공유되어야 한다면 MODE_GLOBAL전략을 이용하면 된다.
하지만 MODE_GLOBAL 전략은 일반적인 애플리케이션에는 잘 이용되지 않는다.
백엔드 웹 애플리케이션은 수신하는 요청을 독립적으로 관리하기 때문에 모든 요청에 대해 하나의 컨텍스트를 이용하기보다 요청별로 SecurityContext 를 분리하는 것이 합리적이다.
다만, 독립형 애플리케이션에는 공유하는 것이 좋은 전략이 될 수도 있다.
MODE_GLOBAL 전략을 이용하게 되면 모든 스레드가 같은 SecurityContext 에 접근한다.
즉, 모든 스레드가 같은 데이터에 접근하고, 변경이 가능하기 때문에 경합 상황이 발생할 수 있으므로 동시 접근 처리를 따로 해주어야 한다. (SecurityContext 는 스레드 안전을 지원하지 않음)
1.4. DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 로 SecurityContext 전달
이 방법보다 1.5.
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService로SecurityContext전달 에 나오는 방법이 더 좋으니 참고만 할 것
기본적으로 프레임워크는 요청 스레드에 SecurityContext 를 제공하고, 이 스레드만 이 SecurityContext 에 접근하도록 보장한다.
따라서 비동기 메서드를 이용하여 새로 생성된 스레드에 대해서는 명시적으로 모드(MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL) 를 설정해야 한다.
하지만 이 경우에도 개발자가 직접 스레드를 생성한 경우는 프레임워크가 새로 생성된 스레드를 모르기 때문에 MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL 로도 해결이 되지 않는다.
이런 스레드를 자체 관리 스레드 라고 한다.
이럴 경우는 개발자가 SecurityContext 를 전파해야 하는데 별도의 스레드에서 실행하고 싶은 작업을 DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 로 장식하면 된다.
DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 는 Runnable 을 확장하며, 반환값이 없는 작업 실행 후 이용 가능하다.
반환값이 있는 작업에는 DelegatingSecurityContextCallable<T> 에 해당하는 Callable<T> 대안을 이용하면 된다.
두 클래스 모두 비동기적으로 실행되는 작업을 나타내며, 작업을 실행하는 스레드를 위해 현재의 SecurityContext 를 복사해준다.
DelegatingSecurityContextCallable 로 현재 컨텍스트를 새로운 스레드에 복사하는 예시
import org.springframework.security.concurrent.DelegatingSecurityContextCallable;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
// `DelegatingSecurityContextCallable` 로 현재 컨텍스트를 새로운 스레드에 복사
@GetMapping("delegatingTest")
public void delegatingTest() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Callable<String> task = () -> {
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
return securityContext.getAuthentication().getName();
};
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
try {
// 현재의 컨텍스트를 새로운 스레드에 제공
DelegatingSecurityContextCallable contextTask = new DelegatingSecurityContextCallable<>(task);
// 실행할 작업을 ExecutorService 에 제출하고 실행
System.out.println(executorService.submit(contextTask).get());
} finally {
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
1.5. DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService 로 SecurityContext 전달
1.4. DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 로 SecurityContext 전달 에서는 작업 자체를 이용하여 SecurityContext 에서 세부 정보를 복사하였다.
위에서 본 DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 과 DelegatingSecurityContextCallable 은 비동기적으로 실행하는 작업을 장식하고, 구현이 새로 생성된 스레드의 SecurityContext 에 접근할 수 있도록 SecurityContext 에서 세부 정보를 복사하는 일을 한다.
하지만 새로운 스레드로의 SecurityContext 전파 시 작업에서 처리하지 않고 스레드 풀에서 전파를 관리하는 더 좋은 방법이 있다.
작업을 장식하는 대신에 특정 유형의 Executor 를 이용하는 것이다.
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService 의 구현은 ExecutorService 를 장식하기 때문에 SecurityContext 전파도 같이 처리된다.
아래는 DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService 가 ExecutorService 를 장식하여 작업을 제출할 때 SecurityContext 세부 정보를 전파하는 예시이다.
package com.assu.study.chap0502.controller;
import org.springframework.security.concurrent.DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
// `DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService` 가 `ExecutorService` 를 장식하여
// 작업을 제출할 때 `SecurityContext` 세부 정보를 전파
@GetMapping("delegatingTest2")
public void delegatingTest2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Callable<String> task = () -> {
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
return securityContext.getAuthentication().getName();
};
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 새로운 스레드로 컨텍스트 전파 시 작업에서 하지 않고 스레드 풀에서 전파 관리
executorService = new DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService(executorService);
try {
System.out.println(executorService.submit(task).get());
} finally {
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
$ curl -w "%{http_code}" -u user:da4f412b-6c4a-4322-aab7-ca8d2fd3d9fc http://localhost:8080/delegatingTest2
200%
1.6. SecurityContext 를 별도의 스레드로 전파하는 객체들
| 클래스 | 설명 |
|---|---|
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutor | - Executor 인터페이스를 구현- Executor 객체를 장식하면 SecurityContext 를 해당 풀에 의해 생성된 스레드로 전달하는 기능을 제공 |
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService | - ExecutorServie 인터페이스를 구현- ExecutorService 객체를 장식하면 SecurityContext 를 해당 풀에 의해 생성된 스레드로 전달하는 기능을 제공 |
DelegatingSecurityContextScheduledExecutorService | - ScheduledExecutorService 인터페이스를 구현- ScheduledExecutorService 객체를 장식하면 SecurityContext 를 해당 풀에 의해 생성된 스레드로 전달하는 기능을 제공 |
DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable | - Runnable 인터페이스를 구현- 다른 스레드에서 실행되며 응답을 반환하지 않는 작업을 나타냄 - Runnable 기능에 더해 새로운 스레드에서 이용하기 위해 SecurityContext 를 전파 가능 |
DelegatingSecurityContextCallable | - Callable 인터페이스를 구현- 다른 스레드에서 실행되며 최종적으로 응답을 반환하는 작업을 나타냄 - Callable 기능에 더해 새로운 스레드에서 이용하기 위해 SecurityContext 를 전파 가능 |
예약된 작업을 위해 SecurityContext 를 전파해야 한다면 DelegatingSecurityContextScheduledExecutorService 데코레이터를 이용하면 된다.
참고 사이트 & 함께 보면 좋은 사이트
본 포스트는 로렌티우 스필카 저자의 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션을 기반으로 스터디하며 정리한 내용들입니다.
- 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션
- Configuration Migrations
- Spring Boot 3.x + Security 6.x 기본 설정 및 변화
- 스프링 부트 2.0에서 3.0 스프링 시큐리티 마이그레이션 (변경점)
