Java8 - CompletableFuture (2): 비동기 연산의 파이프라인화
- 두 개 이상의 비동기 연산을 파이프라인으로 만들고 합치기
- 비동기 작업 완료 대응
소스는 github 에 있습니다.
목차
1. 비동기 작업 파이프라인
모든 상점이 하나의 할인 서비스를 사용하기로 했고, 할인 서비스는 아래와 같이 서로 다른 할인율을 제공한다고 해보자.
할인 서비스(원격이라고 가정)
public class Discount {
public enum Code {
NONE(0), SILVER(1), GOLD(10), PLATINUM(15), DIAMOND(20);
private final int percentage;
Code(int percentage) {
this.percentage = percentage;
}
}
}
1.1. 할인 서비스 구현
이 최저 가격 검색 애플리케이션은 여러 상점에서 가격 정보를 얻고, 결과 문자열을 파싱하고, 할인 서버에 질의를 보낼 준비가 되었다. 할인 서버에서 할인율을 확인해서 최종 가격을 계산할 수 있다.
상점에서 제공한 문자열 파싱은 Quote 클래스로 캡슐화한다.
// 상점에서 얻은 문자열을 static 팩토리 메서드인 parse() 로 넘겨주면 상점 이름, 할인 전 가격, 할인 후 가격 정보를
// 포함하는 Quote 클래스 인스턴스 생성
public class Quote {
private final String shopName;
private final double price;
private final Discount.Code discountCode;
public Quote(String shopName, double price, Discount.Code discountCode) {
this.shopName = shopName;
this.price = price;
this.discountCode = discountCode;
}
// static 팩토리 메서드
public static Quote parse(String s) {
String[] split = s.split(":");
String shopName = split[0];
double price = Double.parseDouble(split[1]);
Discount.Code discountCode = Discount.Code.valueOf(split[2]);
return new Quote(shopName, price, discountCode);
}
public String getShopName() {
return shopName;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public Discount.Code getDiscountCode() {
return discountCode;
}
}
할인 서비스인 Discount 에도 Quote 객체를 인수로 받아 할인된 가격 문자열을 반환하는 메서드를 추가한다.
Discount
// Quote 객체를 인수로 받아 할인된 가격 문자열 반환
public static String applyDiscount(Quote quote) {
return quote.getShopName() + " price is " + Discount.apply(quote.getPrice(), quote.getDiscountCode());
}
private static double apply(double price, Code code) {
delay(); // Discount 는 원격 서비스라고 간주하므로 지연이 있는 것처럼 지연을 줌
return format(price * (100 - code.percentage) / 100);
}
상점의 getPrice() 메서드도 결과 형식을 위에 맞게 변경한다.
Shop.java
public String getPrice(String product) {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
Discount.Code code = Discount.Code.values()[random.nextInt(Discount.Code.values().length)];
return name + ":" + price + ":" + code;
}
BestPrice:123.2:DIAMOND
1.2. 할인 서비스 사용
순차적이면서 동기적으로 가격 조회
// Discount 서비스를 사용하여 제품명 입력 시 상점 이름과 제품가격 반환 (순차, 동기적)
public List<String> findPricesSequential(String product) {
return shops.stream()
.map(shop -> shop.getPrice(product)) // Stream<String> 반환, 각 상점에서 할인 전 가격 조회
.map(Quote::parse) // Stream<Quote> 반환, 상점에서 반환한 문자열을 Quote 객체로 변환
.map(Discount::applyDiscount) // Stream<String> 반환, 할인 서비스를 사용하여 각 Quote 에 할인 적용
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
위 방법은 성능 최적화와는 거리가 멀다.
[BestPrice price is 101.15, CoolPrice price is 171.64, SeventeenPrice price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice1 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice2 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice3 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice4 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice5 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice6 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice7 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice8 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice9 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice10 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice11 price is 140.72, TXTPrice price is 95.41]
findPricesSequentialdone in 30144 ms
상점에서 가격을 얻느라 15초가 소요되고, 상점에서 반환된 가격 정보에 할인 코드를 적용하는 과정에서 또 15초가 소요된다.
병렬 스트림을 사용하면 성능을 개선할 수 있지만 스트림이 사용하는 스레드 풀의 크기가 고정되어 있어서 상점 수가 늘어났을 때처럼 검색 대상이 확장되었을 때 유연하게 대응할 수 없다.
따라서 CompletableFuture 에서 수행하는 태스크를 설정할 수 있는 Executor 를 정의하여 CPU 사용을 극대화한다.
1.3. 동기 작업과 비동기 작업 조합
이제 위 코드를 CompletableFuture 를 이용하여 비동기적으로 재구현한다.
BestPriceFinder.java
// Discount 서비스를 사용하여 제품명 입력 시 상점 이름과 제품가격 반환 (비동기적)
public List<String> findPriceFuture(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<String>> priceFuture = shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor)) // 각 상점에서 할인 전 가격을 비동기적으로 조회
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote::parse)) // 상점에서 반환한 문자열을 Quote 객체로 변환
// 결과 Future 를 다른 비동기 작업과 조합하여 할인 코드 적용
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return priceFuture.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join) // 스크림의 모든 Future 가 종료되길 기다렸다가 각각의 결과 추출
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
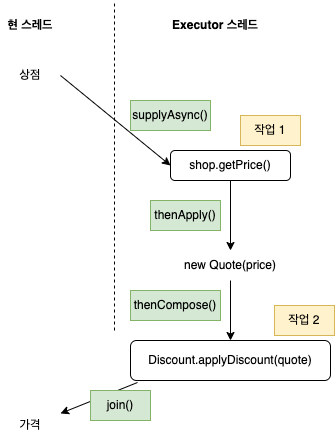
1.3.1. 가격 정보 조회
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor)) // 각 상점에서 할인 전 가격을 비동기적으로 조회
팩토리 메서드인 supplyAsync() 에 람다 표현식을 사용하여 비동기적으로 상점에서 가격 정보를 조회한다.
조회 결과는 Stream<CompletableFuture<String>> 이다.
각 CompletableFuture 는 작업이 끝났을 때 해당 상점에서 반환하는 문자열 정보를 반환한다.
1.3.2. Quote 파싱: CompletableFuture.thenApply()
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote::parse)) // 상점에서 반환한 문자열을 Quote 객체로 변환
결과 문자열을 Quote 로 변환한다.
파싱 동작에는 원격 서비스나 I/O 작업이 없으므로 즉시 지연없이 동작 수행이 가능하다. 따라서 첫 번째 과정에서 생성된 CompletableFuture 에 thenApply() 메서드를 호출한 후 문자열을 Quote 인스턴스로 변환하는 Function 으로 전달한다.
thenApply() 메서드는 CompletableFuture 가 끝날 때까지 블록되지 않는다는 점에 주의한다.
즉, CompletableFuture 가 동작을 완전히 완료한 다음에 thenApply() 메서드로 전달된 람다 표현식을 적용할 수 있다.
따라서 CompletableFuture<String> 을 CompletableFuture<Quote> 로 변환할 것이다.
1.3.3. CompletableFuture 를 조합하여 할인된 가격 계산: CompletableFuture.thenCompose()
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(quote -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)))
상점에서 받은 할인 전 가격에 원격 서비스인 Discount 서비스에서 제공하는 할인율을 적용하는 로직이다.
원격 실행이 포함되므로 동기적으로 작업을 수행한다.
아래처럼 2개의 CompletableFuture 로 이루어진 연쇄적으로 수행되는 두 개의 비동기 동작을 만들 수 있다.
- 상점에서 가격 정보를 얻어와서 Quote 로 변환
- 변환된 Quote 를 Discount 서비스로 전달하여 할인된 최종 가격 조회
CompletableFuture 는 비동기 연산을 파이프라인으로 만들 수 있는 thenCompose() 메서드를 제공한다.
thenCompose() 는 첫 번째 연산의 결과를 두 번째 연산으로 전달한다. (= 첫 번째 CompletableFuture 의 결과가 두 번째 CompletableFuture 의 입력으로 사용됨)
이 Future 가 여러 상점에서 Quote 를 얻는 동안 메인 스레드는 다른 작업을 수행할 수 있다.
위의 map() 까지 수행하고 나면 List<CompletableFuture<String>> 이 반환되는데 CompletableFuture 가 완료되기를 기다렸다가 join() 으로 값을 추출한다.
이제 실행 결과를 보자.
[BestPrice price is 101.15, CoolPrice price is 171.64, SeventeenPrice price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice1 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice2 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice3 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice4 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice5 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice6 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice7 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice8 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice9 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice10 price is 140.72, SeventeenPrice11 price is 140.72, TXTPrice price is 95.41]
findPricesSequentialdone in 30108 ms
[BestPrice price is 105.23, CoolPrice price is 153.41, SeventeenPrice price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice1 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice2 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice3 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice4 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice5 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice6 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice7 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice8 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice9 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice10 price is 111.33, SeventeenPrice11 price is 111.33, TXTPrice price is 130.21]
findPriceFuturedone in 2013 ms
순차적, 동기적으로 수행했을 때는 30초가 소요되었지만 비동기적으로 수행했을 때 2초밖에 안 걸리는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
thenCompose()
이전 작업을 수행한 스레드와 같은 스레드에서 작업을 실행
thenComposeAsync()
다음 작업이 다른 스레드에서 실행되도록 스레드 풀로 작업을 제출
위 예제에서는 두 번째 CompletableFuture 의 결과가 첫 번째 CompletableFuture 에 의존하므로 두 개의 CompletableFuture 를 하나로 조합하던 thenComposeAsync() 를 사용하던 최종 결과와 실행시간에는 영향을 미치지 않는다.
따라서 스레드 전환 오버헤드가 적게 발생하면서 효율이 좋은 thenCompose() 를 사용하였다.
1.4. 서로 독립적인 CompletableFuture 와 서로 비독립적인 CompletableFuture 합치기: CompletableFuture.thenCombine()
바로 위처럼 하나의 CompletableFuture 의 결과가 다른 CompletableFuture 의 입력으로 사용되는 등 서로 비독립적인 CompletableFuture 를 조합할 때는 thenCompose() 를 사용하여 조합한다.
만일 독립적으로 실행된 CompletableFuture 의 결과를 합쳐야 할 때는 thenCombine() 을 사용한다.
thenCombine() 은 BiFunction 두 번째 인수로 받는다.
BiFunction<T,U,R> (T,U) -> R
thenCombine() 은 두 개의 CompletableFuture 의 결과를 어떻게 합칠 지 정의한다.
thenCombineAsync() 는 BiFunction 이 정의하는 조합 동작이 스레드 풀로 제출되면서 별도의 태스크에서 비동기적으로 수행된다.
단순한 연산의 경우 별도의 태스크에서 수행하여 자원을 낭비할 필요가 없으므로 thenCombineAsync() 대신 thenCombine() 을 사용한다.
예를 들어 A 상점은 유로 가격 정보를 제공하는데 고객에게는 항상 달러 가격을 보여주어야 한다고 하면
주어진 상품의 가격을 상점에 요청하는 한편, 원격 환율 교환 서비스를 이용해서 유로와 달러의 환율을 비동기적으로 요청해야 한다.
두 가지 데이터를 얻었으면 가격에 환율을 곱해서 결과를 합칠 수 있다.
이렇게 2 개의 CompletableFuture 의 결과가 생성되고, BiFunction 으로 합쳐진 다음 세 번째 CompletableFuture 를 얻을 수 있다.
public class Exchange {
public static double getRate(Money source, Money dest) {
delay(); // 원격 서비스라 가정하여 지연을 줌
return dest.rate / source.rate;
}
public enum Money {
USD(1.0), EUR(1.5);
private final double rate;
Money(double rate) {
this.rate = rate;
}
}
}
BestPriceFinder.java
// 두 개의 독립적인 CompletableFuture 합치기
public List<String> findPriceInUSD(String product) {
List<CompletableFuture<Double>> priceFutures = new ArrayList<>();
for (Shop shop : shops) {
CompletableFuture<Double> futurePriceInUSD =
// 제품 가격 정보를 요청하는 첫 번째 태스크 생성
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product))
.thenCombine(
// 환율 정보를 요청하는 독립적인 두 번째 태스크 생성
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Exchange.getRate(Exchange.Money.EUR, Exchange.Money.USD)),
// 두 결과를 곱해서 가격과 환율 정보를 합침
(price, rate) -> price * rate);
priceFutures.add(futurePriceInUSD);
}
List<String> prices = priceFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.map(price -> price.toString())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return prices;
}
Shop 의 getPrice() 가 아래와 같이 double 을 리턴하는 코드로 수정해야 위 로직이 오류가 안남
public double getPrice(String product) {
double price = calculatePrice(product);
return price;
}
[74.9246887789165, 114.42404955225545, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 93.81400960102833, 74.83025057430663]
findPriceInUSDdone in 3019 ms
2. CompletableFuture 종료 대응 (비동기 동작 완료에 대응)
위 코드를 모든 검색 결과가 완료될 때까지 사용자가 결과를 볼 수 없다.
이용할 수 있는 가격 정보는 즉시 사용자에게 보여줄 수 있어야 한다.
여기선 get() 이나 join() 으로 CompletableFuture 가 완료될 때까지 블록하지 않고 다른 방식으로 CompletableFuture 의 종료에 대응해본다.
위에선 원격 서비스라고 가정하는 것들에 대해서 동일하게 1초의 지연을 주었지만 실제 지연 시간은 모두 다를 것이고, 어떤 상점은 다른 상점들보다 훨씬 빨리 결과를 제공할 것이다.
이제 1초 말고 0.5~2.5초 사이로 랜덤하게 지연을 주어서 시뮬레이션한다.
Util.java
private static final Random rand = new Random();
// 랜덤하게 지연
public static void randomDelay() {
int delay = 500 + rand.nextInt(2000);
try {
Thread.sleep(delay);
} catch (InterruptedException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
이제 모든 상점에서 가격 정보를 제공할때까지 기다리는 것이 아니라 각 상점에서 가격 정보를 제공할때마다 즉시 보여줄 수 있는 최저 가격 검색 애플리케이션을 구축해본다.
2.1. 최저가격 검색 리팩터링: CompletableFuture.thenAccept()
모든 가격 정보를 포함할 때까지 리스트 생성을 기다리지 않도록 하려면 상점에 필요한 일련의 연산 정보를 하는 CompletableFuture 의 스트림을 직접 제어해야 한다.
public Stream<CompletableFuture<String>> findPriceStream(String product) {
return shops.stream()
.map(shop -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> shop.getPrice(product), executor)) // Stream<CompletableFuture<String>> 반환
.map(future -> future.thenApply(Quote::parse)) // // Stream<CompletableFuture<Quote>> 반환
.map(future -> future.thenCompose(quote ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> Discount.applyDiscount(quote), executor)));
}
이제 위 결과에 네 번째 map() 을 적용한다.
public void printPricesStream(String product) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
CompletableFuture[] futures = findPriceStream(product) // Stream<CompletableFuture<String>> 반환
//.map(f -> f.thenAccept(System.out::println)) // Stream<CompletableFuture<Void>> 반환
.map(f -> f.thenAccept(s -> System.out.println(s + " (done in " + ((System.nanoTime() - start) / 1_000_000) + " msecs)")))
.toArray(size -> new CompletableFuture[size]);
// 가장 느린 상점에서 응답을 받아서 반환된 가격을 출력할 기회를 제공
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).join();
System.out.println("All shops have now responded in " + ((System.nanoTime() - start) / 1_000_000) + " ms");
}
새로 추가한 연산은 단순히 각 CompletableFuture 에 동작을 등록한다. CompletableFuture 에 등록된 동작은 CompletableFuture 의 계산이 끝나면 값을 소비한다.
CompletableFuture 는 thenAccept() 메서드로 이 기능을 제공한다.
thenAccept() 는 Consumer 를 인수로 받는다.
thenAcceptAsync() 는 CompletableFuture 가 완료된 스레드가 아니라 새로운 스레드를 이용해서 Consumer 를 실행한다.
불필요한 콘텍스트 변경을 피하는 동시에 CompletableFuture 가 완료되는 즉시 응답하는 것이 좋으므로 thenAccept() 를 사용한다.
(thenAcceptAsync() 를 사용하면 오히려 새로운 스레드를 이용할 수 있을 때까지 기다려야 할 수도 있음)
Consumer<T>
T -> void
우리는 할인 서비스에서 반환하는 문자열 값을 출력하는 동작을 추가할 예정이다.
thenAccept() 는 CompletableFuture<Void> 를 반환한다.
따라서 마지막 map() 연산은 Stream<CompletableFuture<Void>> 를 반환한다.
또한 가장 느린 상점에서 응답을 받아서 반환된 가격을 출력할 기회를 제공하고 싶다면 스트림의 모든 CompletableFuture/
factory 메서드인 CompletableFuture.allOf() 는 CompletableFuture 배열을 입력받아서 CompletableFuture<Void> 를 반환한다.
모든 CompletableFuture 가 완료되어야 CompletableFuture<Void> 가 완료된다.
따라서 allOf() 가 반환하는 CompletableFuture 에 join() 을 호출하면 원래 스트림의 모든 CompletableFuture 의 실행 완료를 기다릴 수 있다.
이를 이용해서 모든 상점이 결과를 반환했거나 타임아웃이 된 것을 알림으로써 사용자에게 더 이상 기다리지 않아도 된다는 정보를 줄 수 있다.
만일 하나의 작업만 끝나도 되는 상황이라면 anyOf() 를 사용한다.
anyOf() 는 CompletableFuture 배열을 입력으로 받아서 CompletableFuture<Object> 를 반환한다.
CompletableFuture<Object> 는 처음으로 완료한 CompletableFuture 의 값으로 동작을 완료한다.
bestPriceFinder.printPricesStream("CoolPrice");
SeventeenPrice8 price is 140.72 (done in 2062 msecs)
BestPrice price is 101.15 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice6 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice7 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
CoolPrice price is 171.64 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice11 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
TXTPrice price is 95.41 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice3 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice1 price is 140.72 (done in 2062 msecs)
SeventeenPrice10 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice4 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice5 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
SeventeenPrice9 price is 140.72 (done in 2062 msecs)
SeventeenPrice2 price is 140.72 (done in 2061 msecs)
All shops have now responded in 2069 ms
3. 정리하며..
- 한 개 이상의 원격 외부 서비스를 사용하는 긴 동작을 실행할때는 비동기 방식으로 성능과 반응성 향상 가능
CompletableFutures를 이용하여 쉽게 비동기 API 구현 가능- 동기 API 를
CompletableFutures로 감싸서 비동기적으로 소비 가능 CompletableFutures에 콜백을 등록해서Future가 동작을 끝내고 결과를 생산했을 때 어떤 코드를 실행하도록 지정 가능CompletableFutures리스트의 모든 값이 완료될 때까지 기다릴 수도 있고, 하나의 값만 완료되길 기다릴 수도 있음
참고 사이트 & 함께 보면 좋은 사이트
본 포스트는 라울-게이브리얼 우르마, 마리오 푸스코, 앨런 마이크로프트 저자의 Java 8 in Action을 기반으로 스터디하며 정리한 내용들입니다.
