Spring Security - 간단한 애플리케이션 구현
in DEV on SpringSecurity
이 포스트에서는 인증을 구현한 애플리케이션을 구축해본다.
UserDetails인터페이스로 사용자 정의- 맞춤형
UserDetailsService정의 PasswordEncoder의 제공한 구현 이용AuthenticationProvider를 이용한 인증 논리 정의- 양식 로그인 인증 방법 설정
소스는 github 에 있습니다.
목차
- 1. 프로젝트 요구 사항 및 설정
- 2. 사용자 관리 구현
- 3. 맞춤형 인증 논리 구현
- 4. 간단한 페이지 구성
- 5. 애플리케이션 실행
- 6.
DelegtingPasswordEncoder적용 - 참고 사이트 & 함께 보면 좋은 사이트
개발 환경
- 언어: java
- Spring Boot ver: 3.2.2
- Spring ver: 6.1.3
- Spring Security ver: 6.2.1
- IDE: intelliJ
- SDK: JDK 17
- 의존성 관리툴: Maven
1. 프로젝트 요구 사항 및 설정
인증에 성공 시 메인 페이지에서 제품 목록을 보여주는 작은 웹 애플리케이션을 구축해본다.
프로젝트의 요구사항은 아래와 같다.
- 제품 정보와 사용자 정보는 DB 에 저장 (user, authority, product)
- 각 사용자 암호는 bcrypt, scrypt 로 해시됨
- 인증은 표준 로그인 양식이며,
formLogin을 인증 방법으로 구성
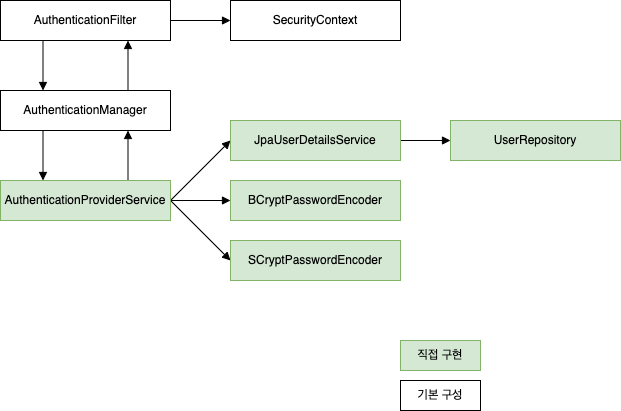
AuthenticationFilter 가 요청을 가로채서 인증 책임을 AuthenticationManager 에게 위임하고, AuthenticationManager 는 AuthenticationProvider 를 이용하여 요청을 인증한다.
인증이 성공하면 AuthenticationFilter 에 의해 SecurityContext 에 인증 정보가 저장된다.
AuthenticationProvider 를 구현한 AuthenticationProviderService 는 UserDetailsService 의 구현인 JpaUserDetailsService 와 각각의 요청된 해싱 알고리즘을 처리하는 PasswordEncoder 를 구현한 BCryptPasswordEncoder, SCryptPasswordEncoder 를 이용한다.
즉, AuthenticationProviderService 는 JpaUserDetailsService 는 DB 에서 사용자 세부 정보를 찾고, BCryptPasswordEncoder, SCryptPasswordEncoder 를 호출하여 암호를 검증하는 인증 논리를 정의한다.
DB Table 스키마는 아래와 같다.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `security`.`user` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`password` TEXT NOT NULL,
`algorithm` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL COMMENT 'BCRYPT, SCRYPT',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`));
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `security`.`authority` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`user_id` INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`));
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `security`.`product` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`price` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`currency` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL COMMENT 'USD, KRW..',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`));
-- 암호는 12345
INSERT IGNORE INTO `security`.`user` (`id`, `username`, `password`, `algorithm`) VALUES ('1', 'assu', '$2a$10$xn3LI/AjqicFYZFruSwve.681477XaVNaUQbr1gioaWPn4t1KsnmG', 'BCRYPT');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `security`.`authority` (`id`, `name`, `user_id`) VALUES ('1', 'READ', '1');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `security`.`authority` (`id`, `name`, `user_id`) VALUES ('2', 'WRITE', '1');
INSERT IGNORE INTO `security`.`product` (`id`, `name`, `price`, `currency`) VALUES ('1', 'APPLE', '10', 'USD');
필요한 종속성은 spring-boot-starter-data-jpa, spring-boot-starter-security, spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf, spring-boot-starter-web, mysql-connector-j 이다.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.assu.study</groupId>
<artifactId>chap0601</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>chap0601</name>
<description>chap0601</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity6</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Data JPA, Hibernate, aop, jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql 관련 jdbc 드라이버와 클래스들 -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.mysql/mysql-connector-j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<scope>annotationProcessor</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
application.properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/security?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
#spring.jpa.defer-datasource-initialization=true
2. 사용자 관리 구현
Spring Security - 사용자 관리,
Spring Security - 암호 처리 와 함께 보면 도움이 됩니다.
스프링 시큐리티에서 사용자 세부 정보를 반환하는 구성 요소는 UserDetailsService이며, 최소한 이 계약을 구현하여 사용자 세부 정보를 가져와야 한다.
아래는 사용자 관리 구현 시 진행할 내용이다.
- 해싱 알고리즘을 위한 암호 인코더 객체 정의
- 사용자 세부 정보를 나타내는 user, authority JPA 엔티티 정의
- JpaRepository 계약 정의
- User JPA 엔티티에 대해
UserDetails계약을 구현하는 데코레이터 생성 UserDetailsService계약 구현
2.1. 암호 인코더 객체 정의
각 사용자 암호는 bcrypt, scrypt 로 해시하므로 구성 클래스에 2개의 PasswordEncoder 를 빈으로 선언한다.
/config/ProjectConfig.java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.scrypt.SCryptPasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
public class ProjectConfig {
// PasswordEncoder 선언
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bcryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
// PasswordEncoder 선언
@Bean
public SCryptPasswordEncoder sCryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new SCryptPasswordEncoder(16384, 8, 1, 32, 64);
}
}
2.2. JPA 엔티티 정의
사용자 세부 정보 조회는 DB 에서 사용자를 검색하는 UserDetailsService 구현을 선언해야 하고, UserDetailsService 는 UserDetails 인터페이스의 구현을 반환해야 한다.
UserDetails 는 DB 에서 조회한 사용자 정보와 권한을 반환하므로 먼저 JPA 엔티티를 정의한다.
/entity/enums/EncryptionAlgorithm.java
public enum EncryptionAlgorithm {
BCRYPT, SCRYPT
}
/entity/enums/Currency.java
package com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.enums;
public enum Currency {
USD, KWR, EUR
}
/entity/User.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.enums.EncryptionAlgorithm;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.util.List;
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private EncryptionAlgorithm algorithm;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "user", fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private List<Authority> authorities;
}
/entity/Authority.java
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
@NoArgsConstructor
@Setter
@Getter
@Entity
public class Authority {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String name;
@JoinColumn(name = "user_id")
@ManyToOne
private User user;
}
/entity/Product.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.enums.Currency;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
@NoArgsConstructor
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double price;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private Currency currency;
}
@Enumerated 애너테이션 보다는 Converter 를 사용하는 것이 더 좋음
그에 대한 상세한 내용은 3. 열거형과 @Enumerated 를 참고하세요.
2.3. JpaRepository 계약 정의
/repository/UserRepository.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Optional;
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {
Optional<User> findByUsername(String username);
}
검색 기능없이 모든 제품을 보여주므로 기본 상속된 findAll() 을 사용한다. 따라서 쿼리 메서드를 따로 명시할 필요는 없다. /repository/ProductRepository.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.Product;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Integer> {
}
2.4. UserDetails 계약 구현
UserDetailsService 에서 사용자를 반환하려면 사용자를 UserDetails 로 나타내야 한다.
아래는 UserDetails 인터페이스를 구현하며, User 엔티티를 래핑하는 예시이다.
/model/CustomUserDetails.java
package com.assu.study.chap0601.model;
import com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.User;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Getter
public class CustomUserDetails implements UserDetails {
private final User user;
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return user.getAuthorities().stream()
.map(a -> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(a.getName())) // DB 에서 조회한 권한명을 SimpleGrantedAuthority 로 매핑
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return user.getPassword();
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return user.getUsername();
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}
2.5. UserDetailsService 계약 구현
이제 사용자 정보를 조회하는 UserDetailsService 를 구현한다.
사용자를 찾으면 CustomUserDetails 인스턴스에서 User 형식의 인스턴스를 래핑하여 반환하고, 사용자를 못 찾으면 UsernameNotFoundException 예외를 발생시킨다.
/service/JpaUserDetailsService.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.User;
import com.assu.study.chap0601.model.CustomUserDetails;
import com.assu.study.chap0601.repository.UserRepository;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class JpaUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public CustomUserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
Supplier<UsernameNotFoundException> supplier =
() -> new UsernameNotFoundException("Username not Found..!");
User user = userRepository.findUserByUsername(username).orElseThrow(supplier);
// User 인스턴스를 CustomUserDetails 로 래핑하여 반환
return new CustomUserDetails(user);
}
}
Supplier<T>에 대한 내용은 2. 함수형 인터페이스 사용 을 참고하세요.
3. 맞춤형 인증 논리 구현
Spring Security - 암호 처리,
Spring Security - 인증 구현(1): AuthenticationProvider,
Spring Security - 인증 구현(2): SecurityContext,
Spring Security - 인증 구현(3): HTTP Basic 인증 와 함께 보면 도움이 됩니다.
인증 논리를 구현하려면 AuthenticationProvider 를 구현해야 한다.
인증 논리를 작성하려면 UserDetailsService 와 PasswordEncoder 가 필요하다.
그리고 AuthenticationProvider.authenticate() 에 인증 논리를 정의하고, AuthenticationProvider.supports() 에 지원하는 인증 형식을 정의한다.
AuthenticationProvider.supports() 구현 시엔 지원되는 인증 형식을 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 으로 정의한다.
/service/AuthenticationProviderService.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.model.CustomUserDetails;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.scrypt.SCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class AuthenticationProviderService implements AuthenticationProvider {
private final JpaUserDetailsService jpaUserDetailsService;
private final BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder;
private final SCryptPasswordEncoder sCryptPasswordEncoder;
/**
* 인증 논리 구현
* <p>
* 사용자 이름에 맞는 사용자를 로드한 후 암호가 DB 에 저장된 해시와 일치하는지 검증
* 검증 작업은 사용자 암호를 해시하는데 이용된 알고리즘에 따름
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
// UserDetailsService 에서 사용자 검색
CustomUserDetails user = jpaUserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
Authentication result;
try {
result = switch (user.getUser().getAlgorithm()) {
case BCRYPT -> checkPassword(user, password, bCryptPasswordEncoder);
case SCRYPT -> checkPassword(user, password, sCryptPasswordEncoder);
};
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Bad credentials...! (authenticate())");
}
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
// UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 는 Authentication 인터페이스의 한 구현이며,
// 사용자 이름과 암호를 이용하는 표준 인증 요청을 나타냄
return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
/**
* 매개 변수로 전달된 PasswordEncoder 를 사용하여 사용자 입력으로 받은 원시 암호가 DB 의 인코딩과 일치하는지 검증 후
* 암호가 올바르면 Authentication 계약의 구현을 인스턴스로 반환
*/
private Authentication checkPassword(CustomUserDetails user, String rawPassword, PasswordEncoder encoder) {
// 인코딩된 문자열(암호)이 원시 암호(rawPassword) 와 일치하는지 확인
if (encoder.matches(rawPassword, user.getPassword())) {
// 암호가 일치하면 AuthenticationProvider 는
// 필요한 세부 정보가 담긴 Authentication 계약의 구현을 '인증됨' 으로 표시한 후 반환함
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.getAuthorities());
} else {
// 암호가 일치하지 않으면 AuthenticationException 형식의 예외 발생
throw new BadCredentialsException("Bad credentials..!");
}
}
}
이제 위에서 구현한 AuthenticationProvider 계약의 구현을 구성 클래스에 등록하고, 양식 기반 인증 방식을 사용하도록 설정한다. /config/SecurityConfig.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.service.AuthenticationProviderService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.ProviderManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configuration.AuthenticationConfiguration;
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SecurityConfig {
private final AuthenticationProviderService authenticationProviderService;
private final AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration;
/**
* 맞춤 구성한 AuthenticationProviderService 구현 연결
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
ProviderManager providerManager = (ProviderManager) authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();
providerManager.getProviders().add(this.authenticationProviderService);
return authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();
}
}
/config/ProjectConfig.java
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.Customizer;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.scrypt.SCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Configuration
public class ProjectConfig {
// PasswordEncoder 선언
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bcryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
// PasswordEncoder 선언
@Bean
public SCryptPasswordEncoder sCryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new SCryptPasswordEncoder(16384, 8, 1, 32, 64);
}
// 양식 기반 인증 방식
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(authz -> authz.anyRequest()
.authenticated())
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults()) // HTTP Basic 인증도 사용
.formLogin(f -> f.defaultSuccessUrl("/main", true)); // 인증 성공 시 /main 으로 이동
// http.authorizeHttpRequests(authz -> authz.anyRequest()
// .authenticated())
// .httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults())
// .formLogin(f -> {
// f.successHandler(customAuthenticationSuccessHandler);
// f.failureHandler(customAuthenticationFailureHandler);
// });
return http.build();
}
}
4. 간단한 페이지 구성
제품 정보를 가져오는 서비스를 구성한다.
/service/ProductService.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.entity.Product;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
public List<Product> findAll() {
return productRepository.findAll();
}
}
/controller/MainController.java
import com.assu.study.chap0601.repository.ProductService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class MainController {
private final ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("main")
public String main(Authentication authentication, Model model) {
// UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken [Principal=assu, Credentials=[PROTECTED], Authenticated=true, Details=null, Granted Authorities=[READ, WRITE]]
System.out.println("controller authentication: " + authentication);
model.addAttribute("username", authentication.getName());
model.addAttribute("products", productService.findAll());
return "main.html";
}
}
/resources/templates/main.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Products</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 th:text="'Hello, ' + ${username} + '!'"/>
<p><a href="/logout">Sign out here</a></p>
<h2>These are all the products:</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th> Name</th>
<th> Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:if="${#lists.isEmpty(products)}">
<td colspan="2"> No Products Available</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="book : ${products}">
<td><span th:text="${book.name}"> Name </span></td>
<td><span th:text="${book.price}"> Price </span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>
5. 애플리케이션 실행
이제 localhost:8080 으로 접속 후 assu / 12345 로 로그인하면 /main 으로 리디렉션되며, 제품의 리스트가 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
6. DelegtingPasswordEncoder 적용
여러 방식으로 암호가 해시되니 DelegtingPasswordEncoder 를 적용하여 코드를 간소화할 수 있다.
아래 내용만 수정해주면 된다.
/config/ProjectConfig.java
// PasswordEncoder 선언
// @Bean
// public BCryptPasswordEncoder bcryptPasswordEncoder() {
// return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
// }
//
// // PasswordEncoder 선언
// @Bean
// public SCryptPasswordEncoder sCryptPasswordEncoder() {
// return new SCryptPasswordEncoder(16384, 8, 1, 32, 64);
// }
// delegatingPasswordEncoding 적용 시
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
/service/AuthenticationProviderService.java
package com.assu.study.chap0601.service;
import com.assu.study.chap0601.model.CustomUserDetails;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class AuthenticationProviderService implements AuthenticationProvider {
private final JpaUserDetailsService jpaUserDetailsService;
// delegatingPasswordEncoding 적용 시 주석 처리
// private final BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder;
// private final SCryptPasswordEncoder sCryptPasswordEncoder;
private final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
/**
* 인증 논리 구현
* <p>
* 사용자 이름에 맞는 사용자를 로드한 후 암호가 DB 에 저장된 해시와 일치하는지 검증
* 검증 작업은 사용자 암호를 해시하는데 이용된 알고리즘에 따름
*/
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
// UserDetailsService 에서 사용자 검색
CustomUserDetails user = jpaUserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
Authentication result;
try {
// delegatingPasswordEncoding 적용 시
result = checkPassword(user, password, passwordEncoder, user.getUser().getAlgorithm().toString());
// result = switch (user.getUser().getAlgorithm()) {
// case BCRYPT -> checkPassword(user, password, bCryptPasswordEncoder);
// case SCRYPT -> checkPassword(user, password, sCryptPasswordEncoder);
// };
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new BadCredentialsException("Bad credentials...! (authenticate())", e);
}
return result;
}
// ...
/**
* 매개 변수로 전달된 PasswordEncoder 를 사용하여 사용자 입력으로 받은 원시 암호가 DB 의 인코딩과 일치하는지 검증 후
* 암호가 올바르면 Authentication 계약의 구현을 인스턴스로 반환
*/
private Authentication checkPassword(CustomUserDetails user, String rawPassword, PasswordEncoder encoder, String algorithm) {
// delegatingPasswordEncoding 적용 시 key 설정
String userPassword = "{" + algorithm.toLowerCase() + "}" + user.getPassword();
// 인코딩된 문자열(암호)이 원시 암호(rawPassword) 와 일치하는지 확인
if (encoder.matches(rawPassword, userPassword)) {
// 암호가 일치하면 AuthenticationProvider 는
// 필요한 세부 정보가 담긴 Authentication 계약의 구현을 '인증됨' 으로 표시한 후 반환함
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.getAuthorities());
} else {
// 암호가 일치하지 않으면 AuthenticationException 형식의 예외 발생
throw new BadCredentialsException("Bad credentials..!");
}
}
}
참고 사이트 & 함께 보면 좋은 사이트
본 포스트는 로렌티우 스필카 저자의 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션을 기반으로 스터디하며 정리한 내용들입니다.
- 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션
- Configuration Migrations
- Spring Boot 3.x + Security 6.x 기본 설정 및 변화
- 스프링 부트 2.0에서 3.0 스프링 시큐리티 마이그레이션 (변경점)
- Password strength: wiki
